Gastric Bypass surgery is a restrictive/malabsorptive surgical procedure. It is restrictive in the sense that it “restricts” how much food the stomach can hold and is “malabsorptive” in that it affects how food and calories are absorbed into the bloodstream. This combination surgery has the highest success rate for amount of weight lost.
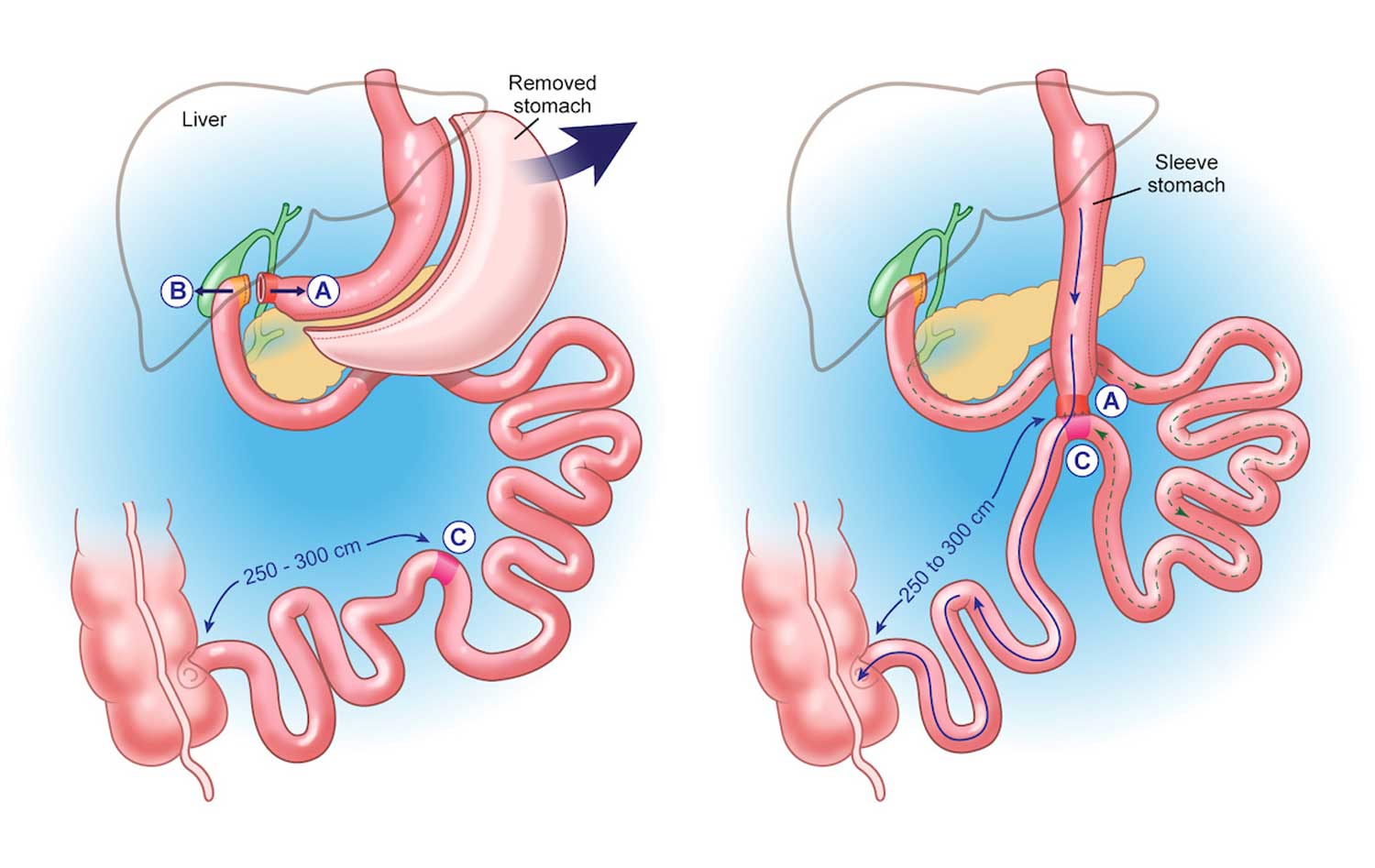
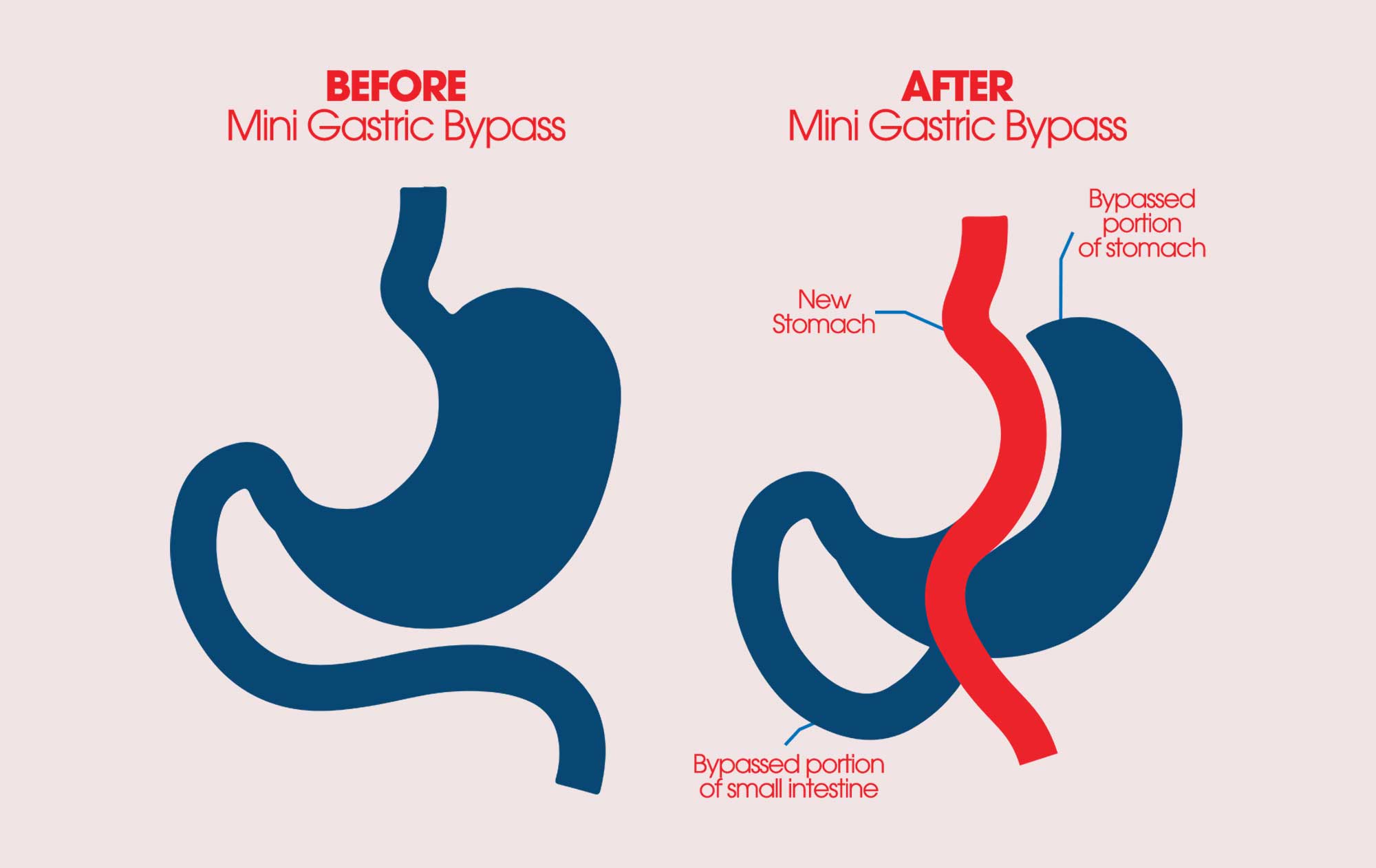
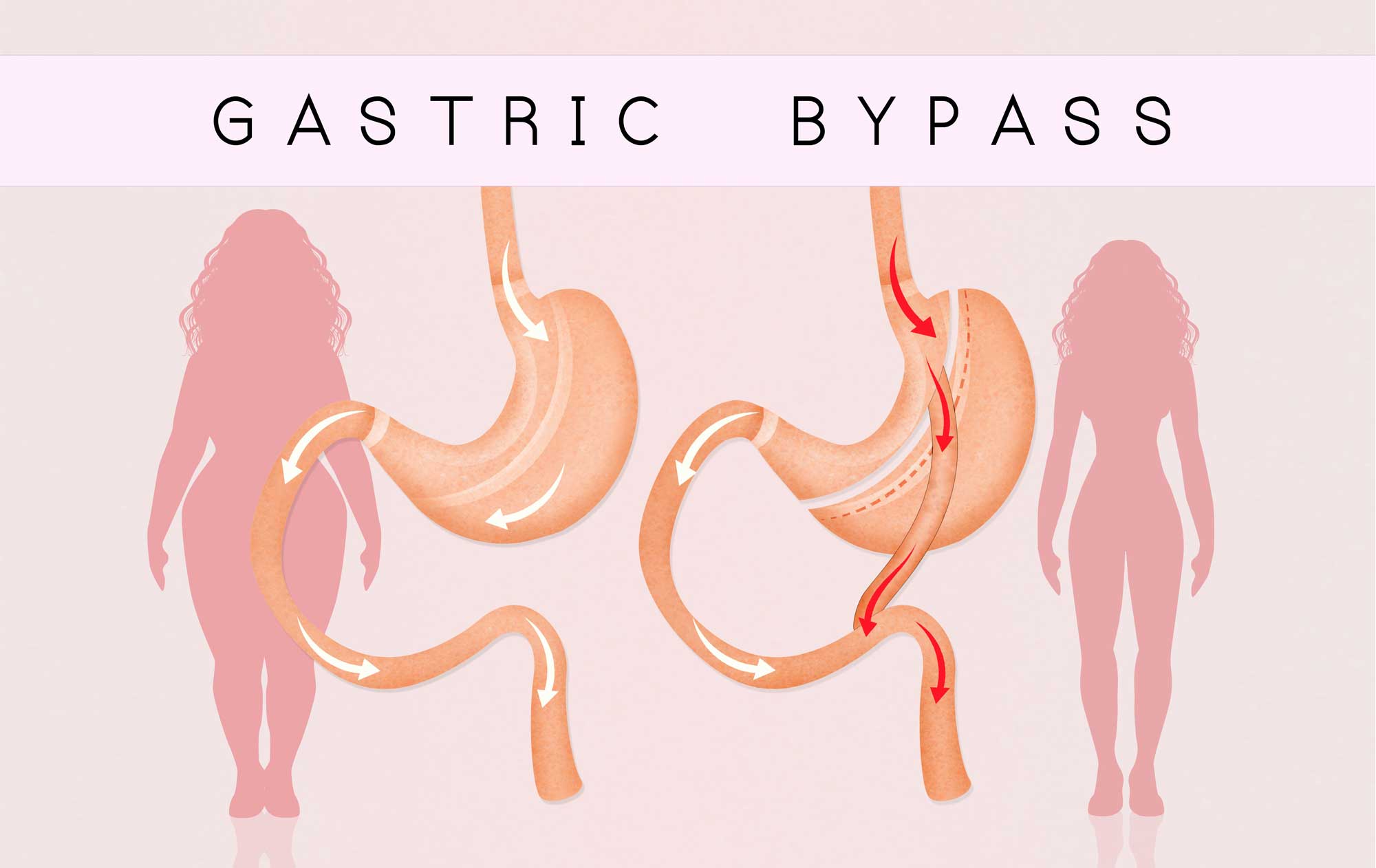
The most common gastric bypass surgery is the Roux-en-Y. This surgery can be done Laparoscopically (keyhole surgery) or through a larger open incision. Your surgeon will decide which option is best for you. In this surgery, the surgeon creates a small stomach pouch by stapling along the upper part of the stomach. A new opening from this pouch is created as well. The small intestine is then cut into two sections. The lower section of intestine is attached to the opening in the stomach pouch creating what is referred to as the “roux limb“. The upper section of the small intestine which carries digestive juices from the remaining portion of the stomach is attached at the distal end of the roux limb. The roux limb enables food to bypass the lower stomach, duodenum, and a portion of the small intestine.
Advantages of Gastric Bypass Surgery
- Quick and dramatic weight loss
- Continued weight loss for 18-24 months post-surgery
- Many patients maintain a weight loss of 60-70% of excess weight 10 years post-op
- Improved health problems associated with severe obesity (i.e. Diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, etc.)
- Improved mobility and quality of life
Disadvantages of Gastric Bypass Surgery
- Major surgery with serious risks
- Malnourishment and anemia may occur requiring lifelong vitamin and mineral supplementation
- Requires permanent lifelong changes to patient’s diet and lifestyle
- Increased risk of gallstones due to rapid weight loss
- Dumping syndrome: nausea, reflux, diarrhea can occur after ingesting high sugar foods
- Hospital stay of 3-5 days usually
- Risk of hair loss
Risks & Complications
- DVT (blood clot in the deep leg veins)
- Damage to adjacent organs
- Leakage of digestive contents from the staple line can lead to serious infection
- Stricture (narrowing) of the opening between the stomach and small intestine
- Dumping Syndrome: Vomiting, reflux, and diarrhea caused by stomach contents moving too rapidly through the small intestine
- Abdominal hernias
- Gallstones
- Dehydration
- Bleeding ulcers of the stomach
- Intolerance to some foods
Photo from: https://www.lm.be