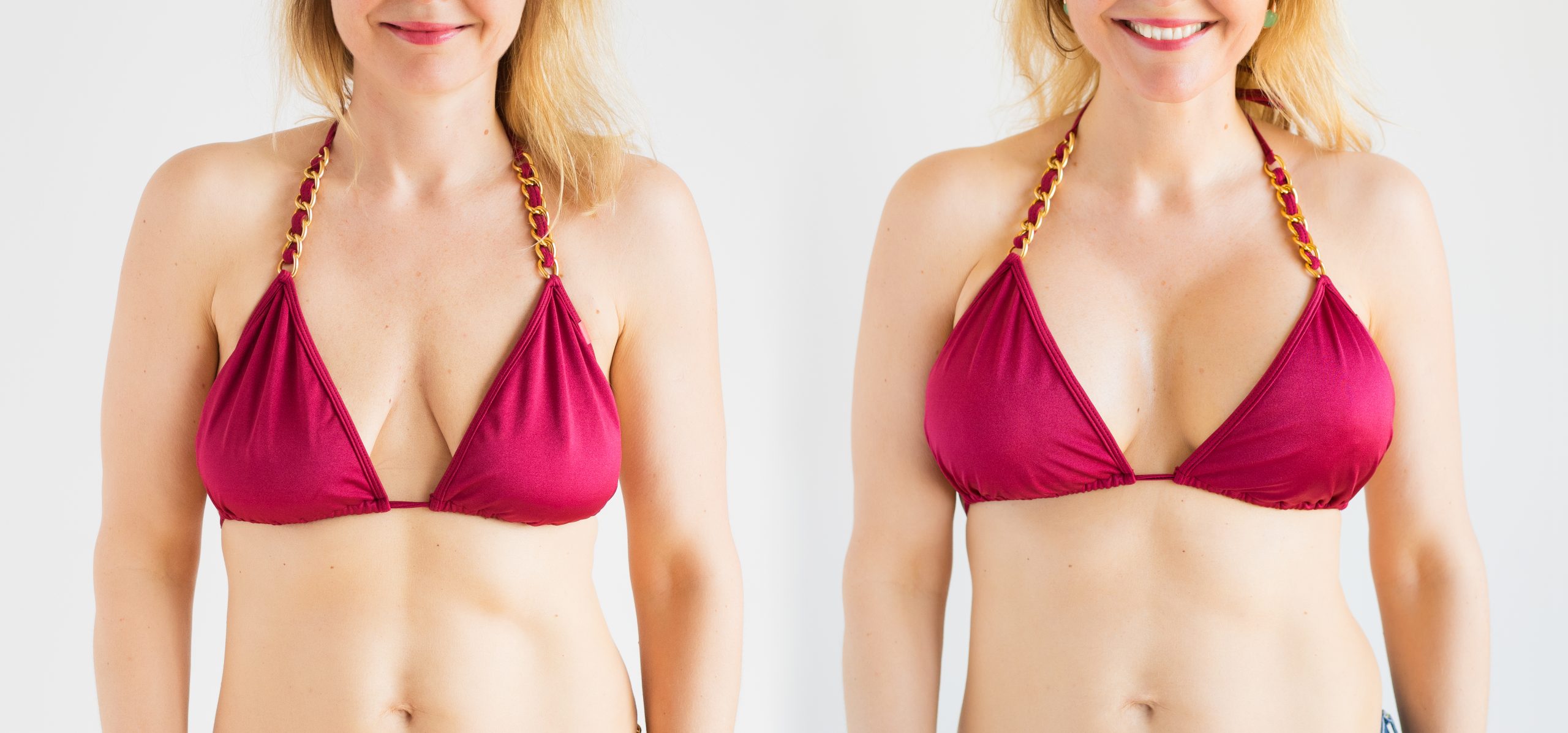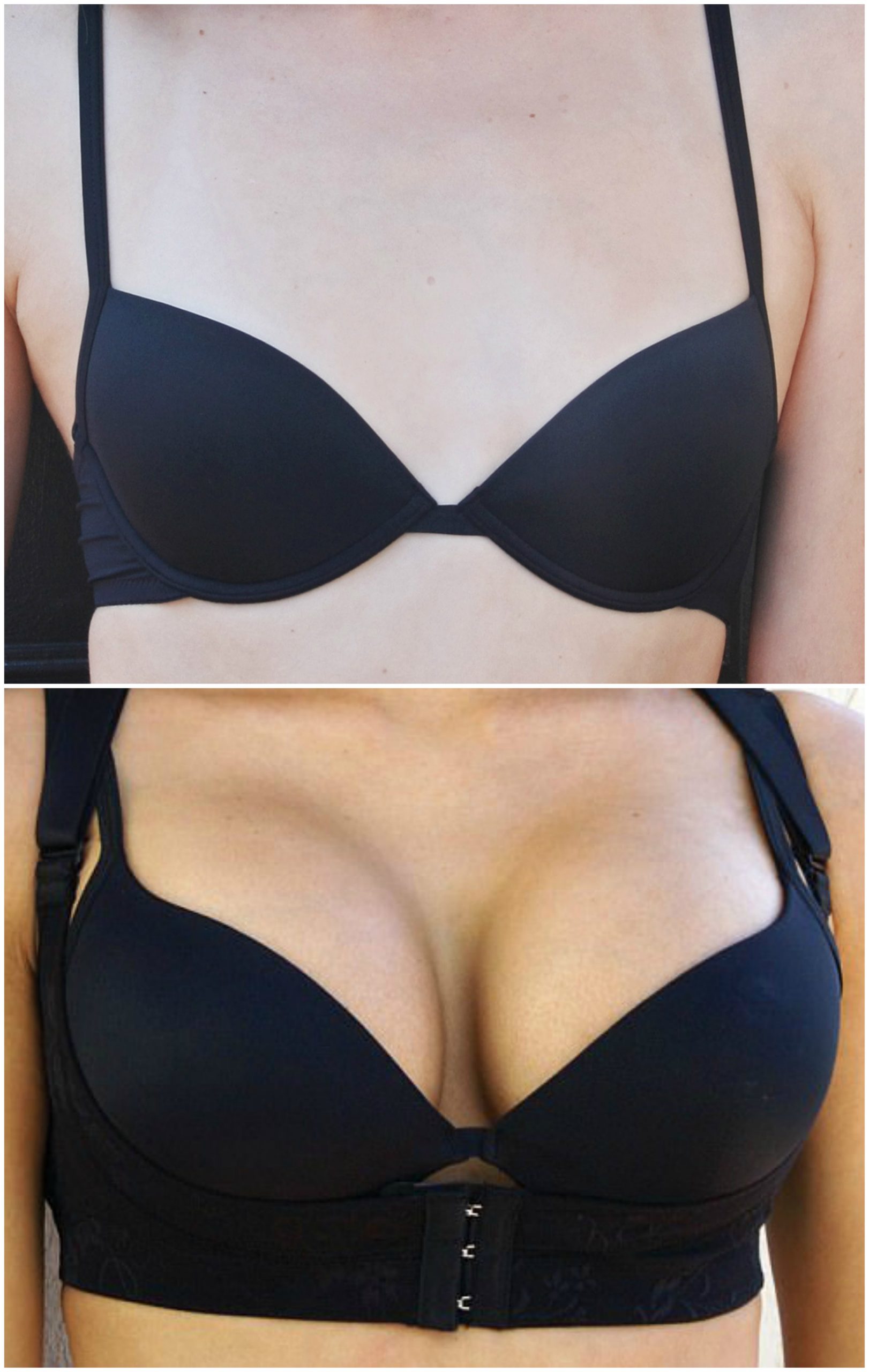
The Procedure
Breast enlargement surgery can be done using general anesthesia, or local anesthesia combined with sedation. Most breast augmentation is done on an outpatient basis.
After making an incision, the surgeon will lift your skin and breast tissue to make a pocket either right behind the breast tissue or under your chest wall muscle. He or she will then insert the implant and center it under your nipples. The incision is closed with stitches. The surgeon repeats the process on the other breast. Gauze bandages may be placed over your breasts to help speed healing.
After Breast Enlargement Surgery
You will probably feel tired and very sore for the first few days after surgery, but your surgeon will encourage you to get up and walk around immediately after surgery. He or she will prescribe pain medication to relieve the discomfort. Your breasts will look bruised and swollen and your nipples may burn for the first 2 weeks after surgery. The stitches are removed a week to 10 days after surgery. The soreness and swelling usually last about 3 to 5 weeks.
You may be able to go back to work in a few days. Your surgeon will tell you when you can begin exercising or lifting. Your scars will stay noticeably pink for several months and then begin to fade, although they will never disappear completely.
The most common complication of breast enlargement surgery is capsular contracture, in which scar tissue around the implant contracts and becomes tight. The tightening scar squeezes the implant, making the breast feel hard. Surgeons can treat this condition by surgically removing the scar tissue or making parallel cuts in it to widen it and make it more elastic. Another option is to remove or replace the implant.
Other possible complications of breast enlargement surgery include excessive bleeding, infection, and numbness of the nipples or incisions. Sensation usually returns over time but loss of sensation can sometimes be permanent. Breast implants can break or leak after an injury or, occasionally, during routine activity. If an implant leaks, your body will absorb the saline solution contained in the implant, but the implant itself must be removed and replaced. Before having the surgery, make sure you talk with your surgeon about the risks and possible complications.