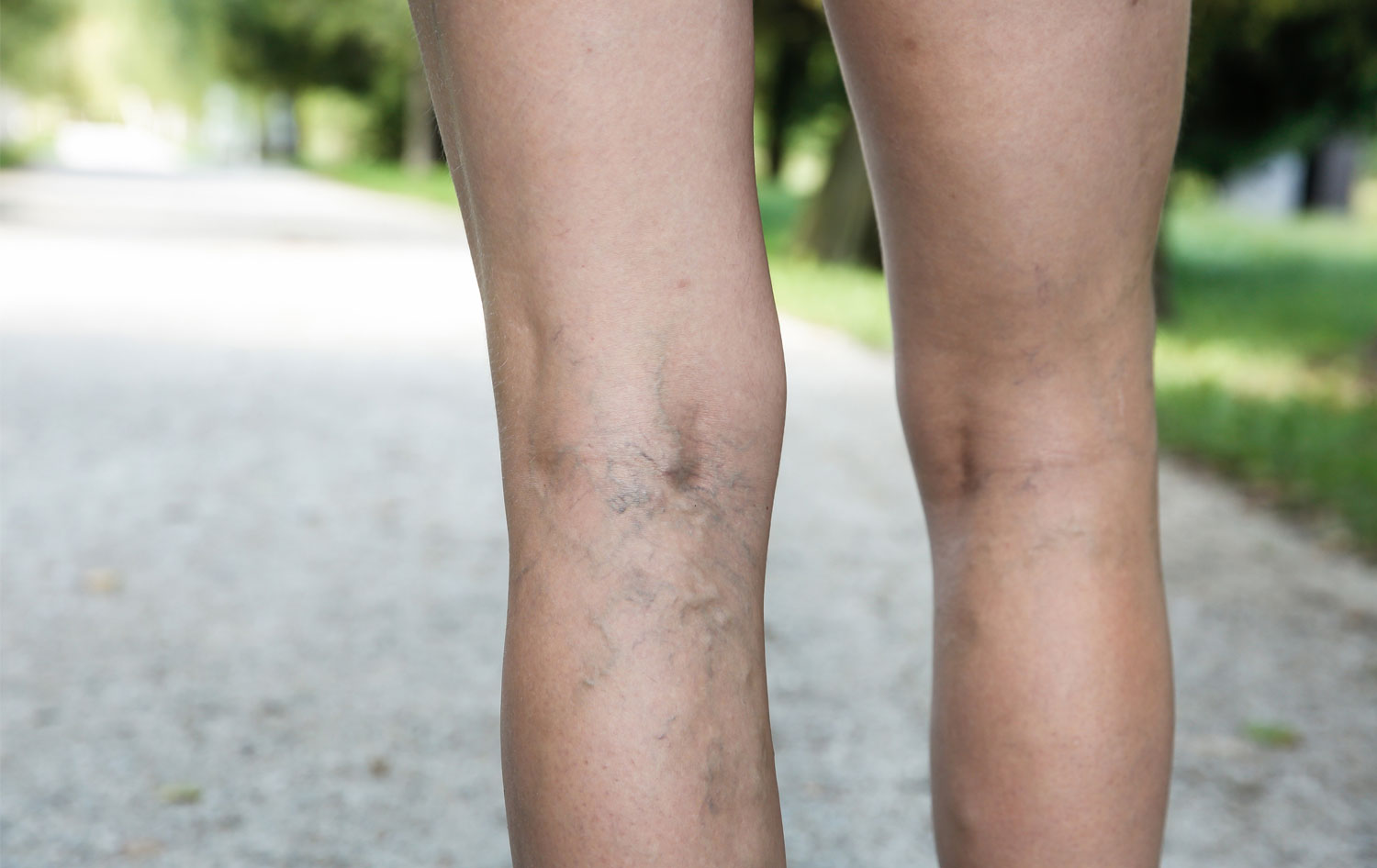
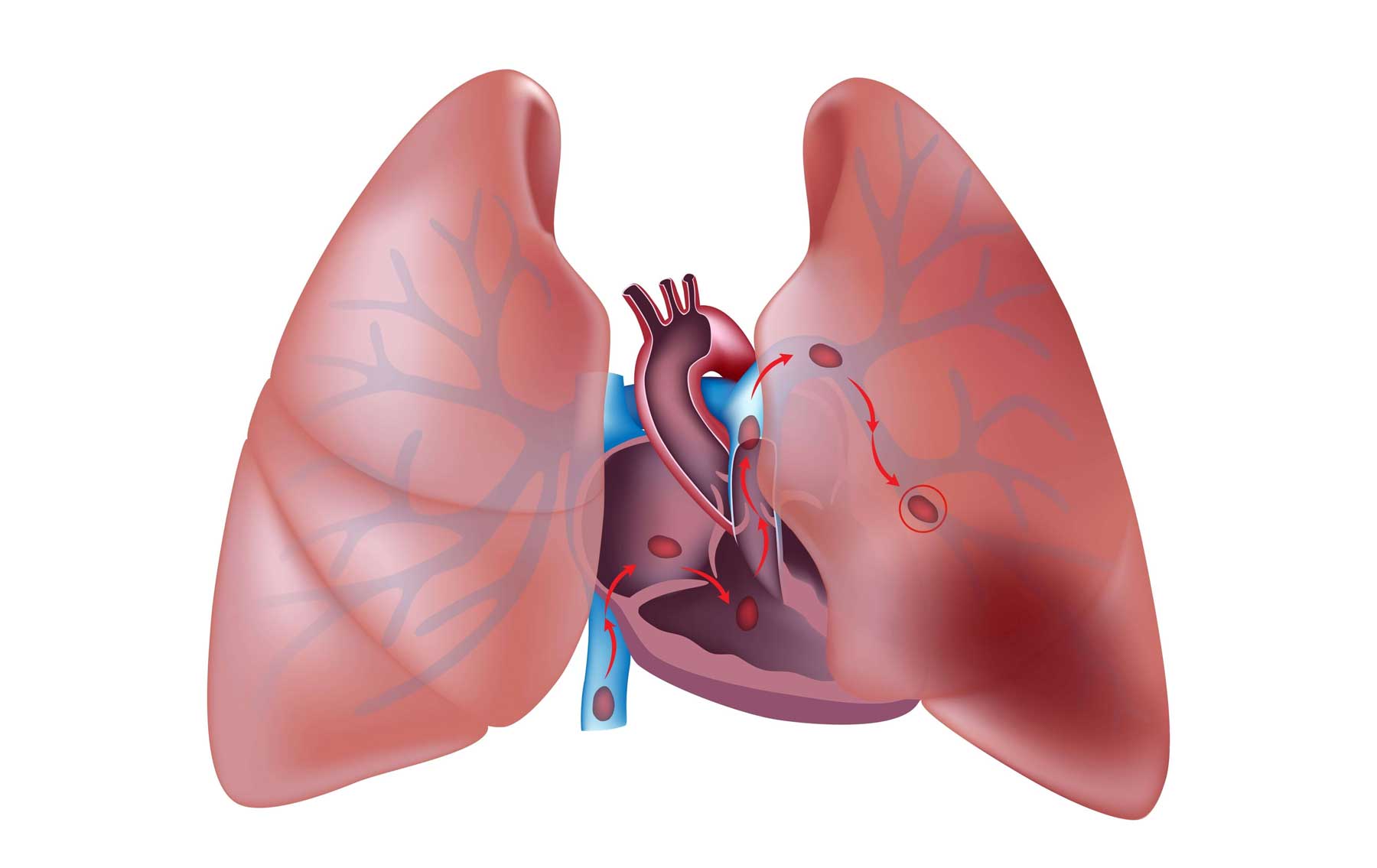
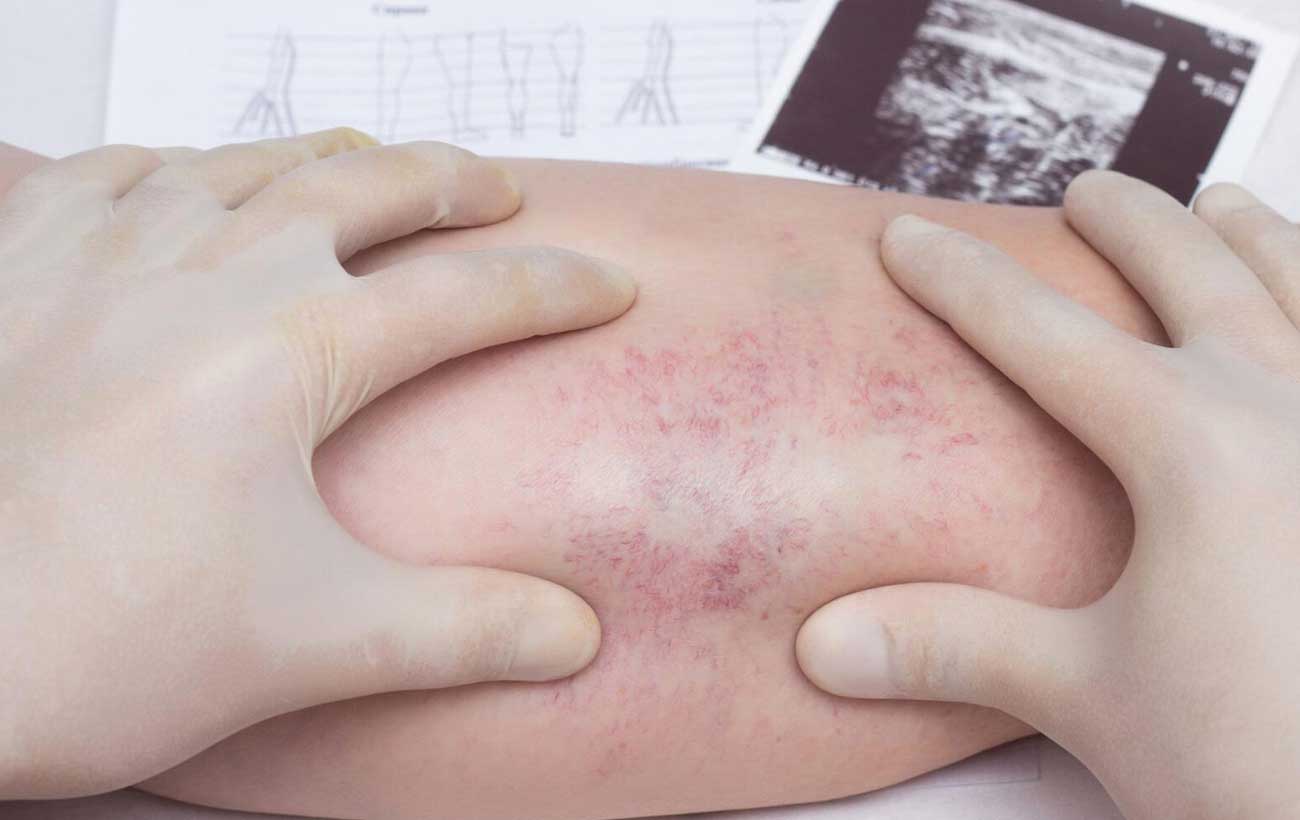
Deep Vein Thrombosis Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot (thrombus), which can partially…
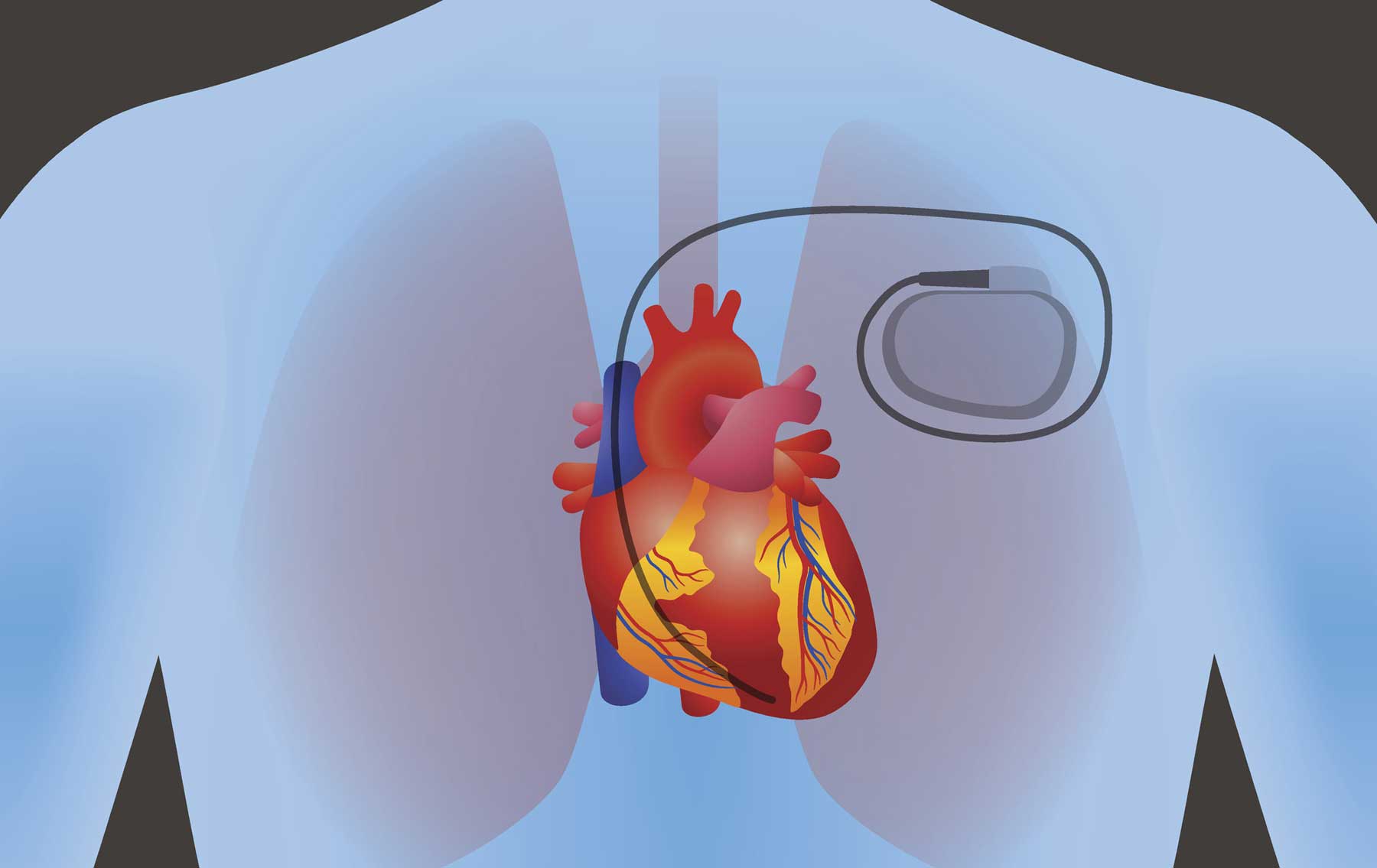
Heart Block
The heart rate is controlled by a natural pacemaker called the sinoatrial node, a group of specialized cells in the wall of the right atrium (the upper right chamber of the heart). The sinoatrial node transmits electrical impulses between the atria and ventricles (the lower chambers of the heart), causing rhythmic contractions of the heart muscle, or heartbeats. If the sinoatrial node malfunctions, the beating of the atria is not coordinated with the beating of the ventricles.
In first-degree heart block, the electrical impulses take longer to travel from the atria to the ventricles. In second-degree heart block, some of the electrical impulses fail to reach the ventricles, causing an irregular heartbeat. In third-degree heart block, electrical impulses do not reach the ventricles, which continue beating slowly, independently of the sinoatrial node and the atria.
In healthy people, the heart rate increases during times of increased demand on the circulatory system, such as during exercise or periods of emotional stress. But in people who have heart block, heart rate does not increase despite an increased demand for blood, and the brain and other body tissues do not receive enough blood and oxygen to function properly.
Heart block often occurs as a result of heart disease or a heart attack. An overdose of a digitalis drug used to treat an irregular heartbeat can also cause heart block. In some people, heart block occurs for no obvious reason. The risk of heart block increases with age, and the disorder occurs most often in older people.
Symptoms
In most people, first-degree and second-degree heart block usually do not produce symptoms. Third-degree heart block may cause sudden loss of consciousness, seizures, or stroke. In some people, third-degree heart block may produce symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath or fatigue. If you are an older person and you have episodes of dizziness, weakness, or confusion, see your doctor as soon as possible. Although these symptoms have many possible causes, early detection and treatment of heart block may save your life.
Treatments
If the doctor has determined that your heart’s natural pacemaker is causing your symptoms, he or she may recommend temporary or permanent insertion of an artificial pacemaker to regulate the heartbeat.