Deep Vein Thrombosis Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot (thrombus), which can partially…
Thrombophlebitis
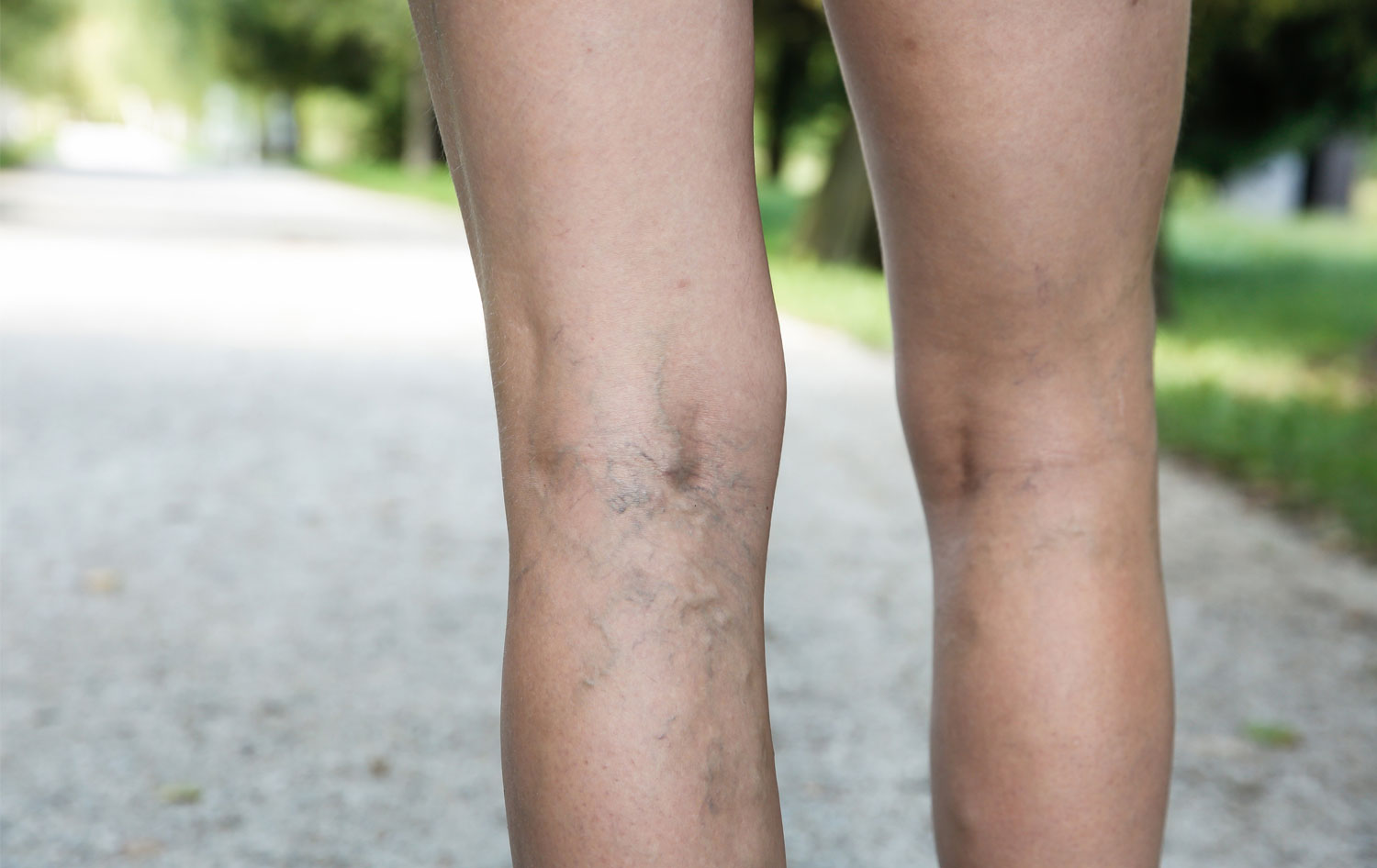
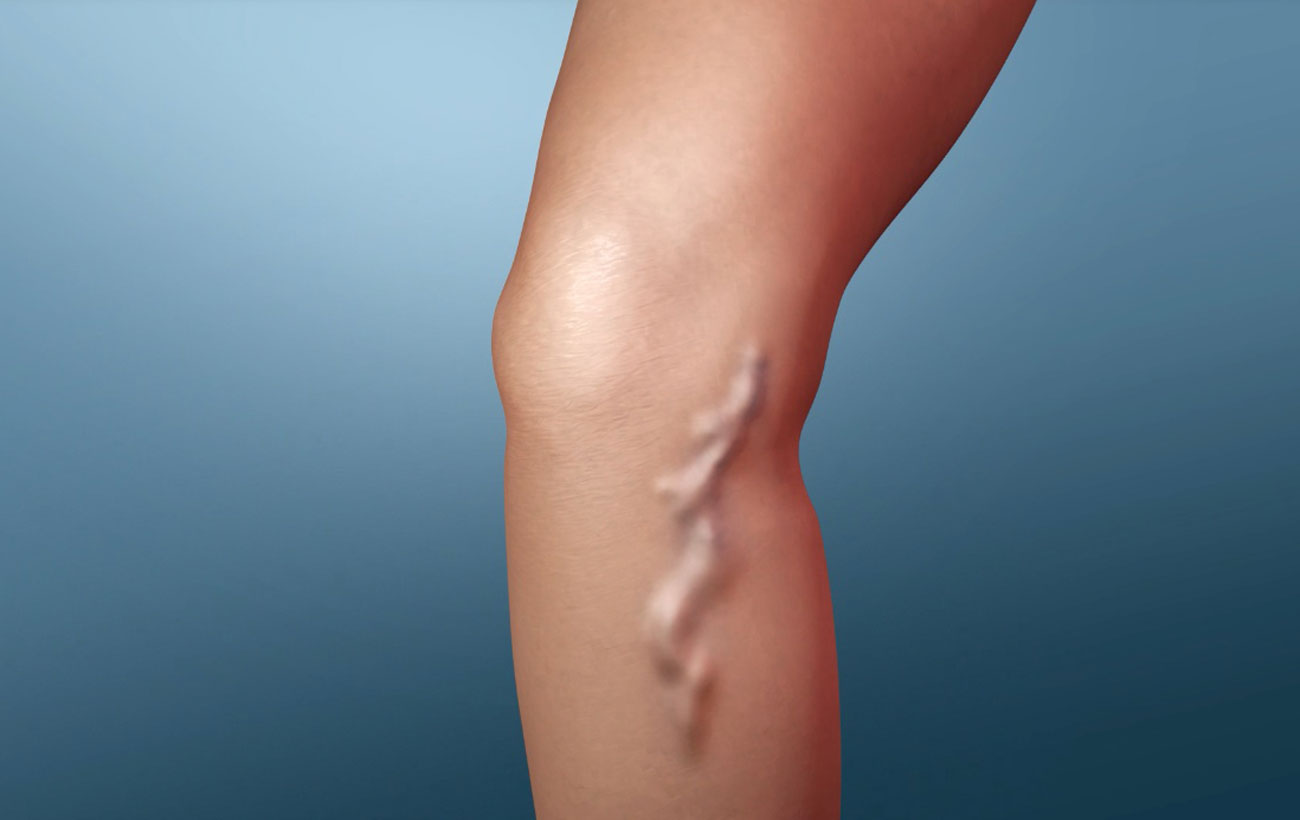
Phlebitis is inflammation of a vein, usually caused by infection or injury. When phlebitis occurs, blood flow through the roughened, swollen vein may become sluggish, encouraging blood clots (thrombi) to develop and adhere to the walls of the vein. This condition, called thrombophlebitis, often occurs in the superficial veins in the legs. In rare cases, thrombophlebitis occurs in the arms.
Women are slightly more likely to develop thrombophlebitis than men. The condition also occurs more frequently in people who have varicose veins. In rare cases, people who are undergoing medical treatment that involves piercing the veins with needles (such as inserting an intravenous line) develop thrombophlebitis.
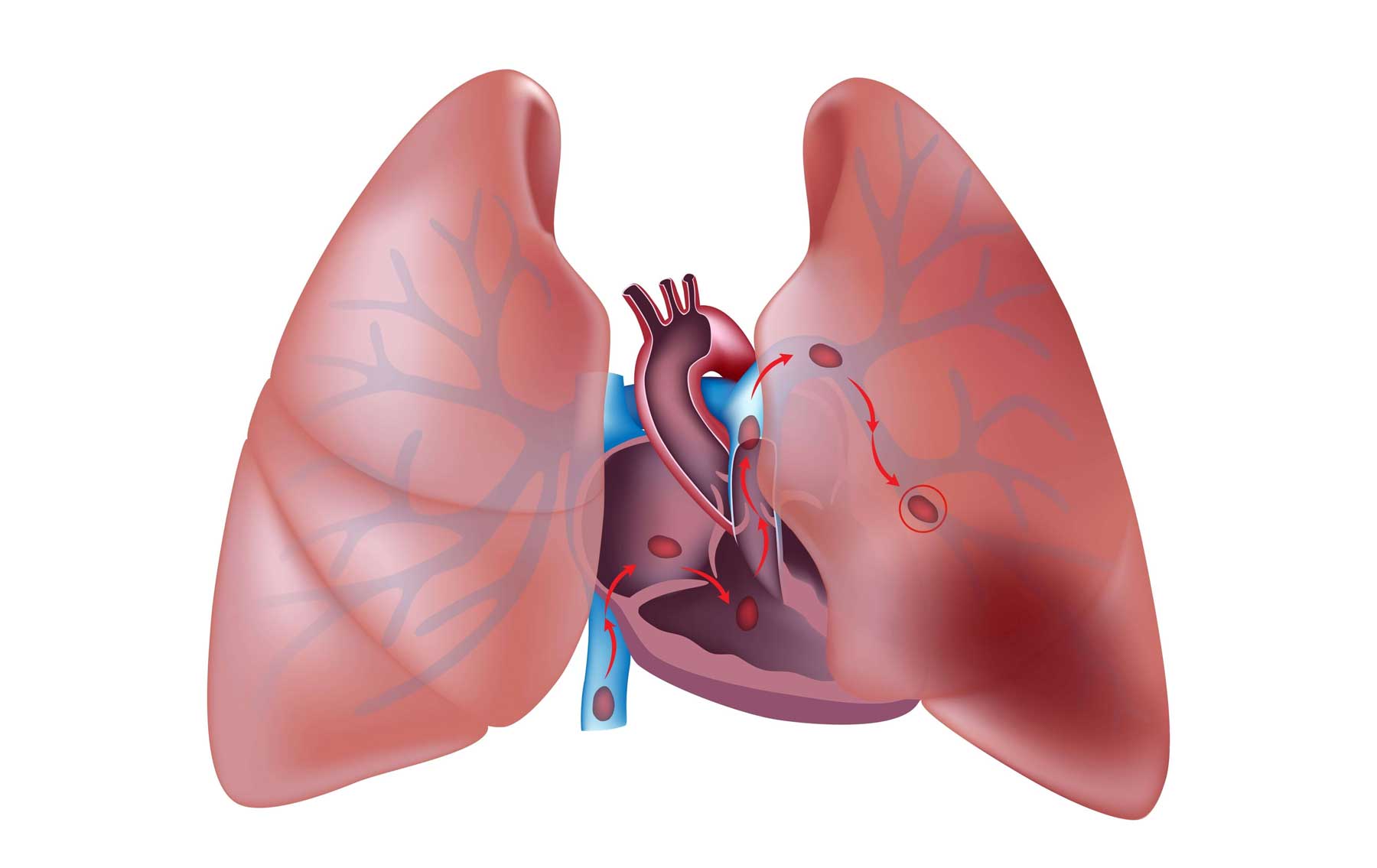
An untreated infection can lead to blood poisoning. There is also a very slight chance that blood clots break off, travel through the bloodstream, and block a blood vessel. However, the most serious risk of thrombophlebitis is that the clot may travel to a more vulnerable spot, such as a deeper vein, most likely in the leg or pelvic area.
Symptoms
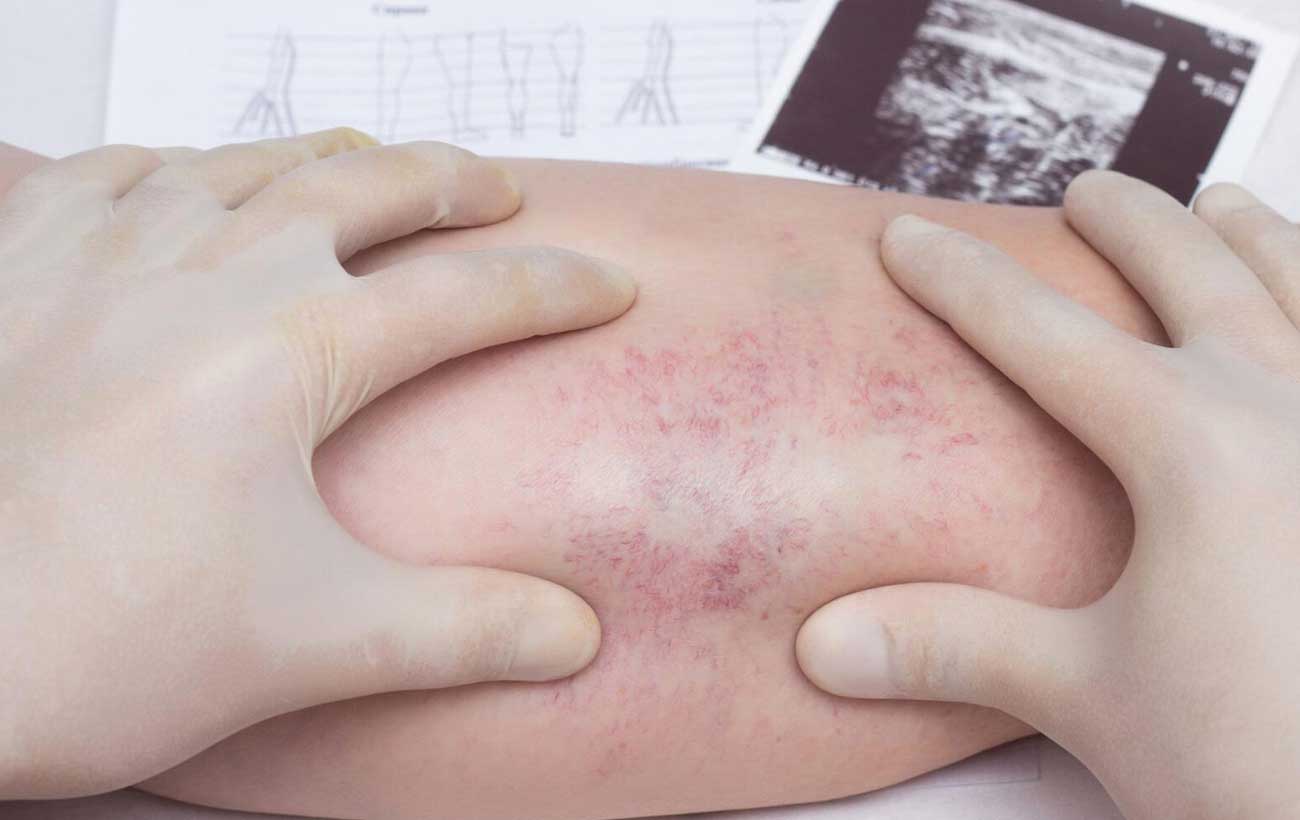
The main symptoms of thrombophlebitis are pain, redness, warmth, tenderness, itching, or swelling under the skin along the length of the affected vein. If the area is infected, you may also have a fever.
Treatments
If you have thrombophlebitis, your doctor may recommend that you take a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug such as aspirin or ibuprofen to relieve pain and inflammation. If you have an infection, he or she may prescribe an antibiotic. The doctor may also recommend that you rest frequently, elevate the affected leg, and apply warm, moist compresses to the affected area. A nonprescription zinc oxide ointment can help relieve itching; ask your doctor to recommend one. The doctor also may recommend that you wear elastic support stockings. With treatment, thrombophlebitis usually clears up within a few weeks.