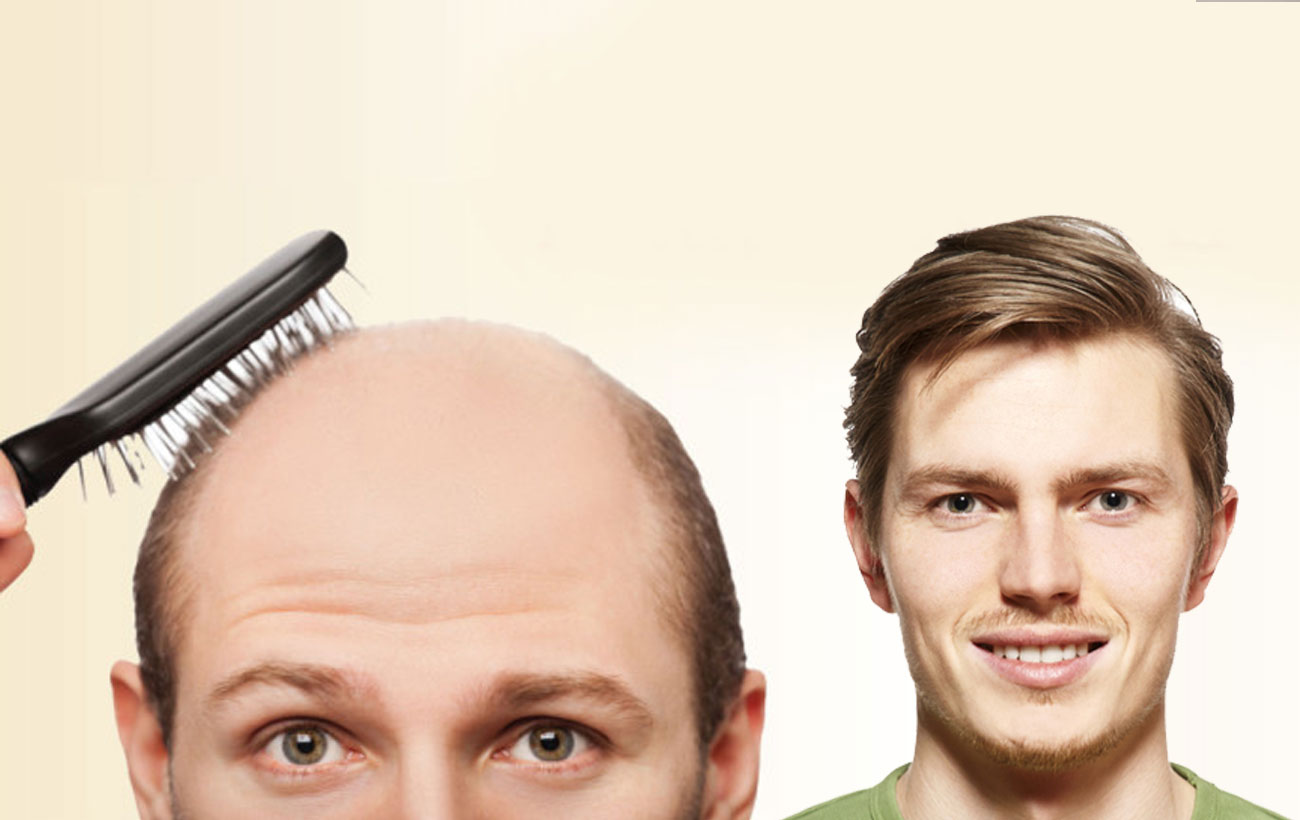
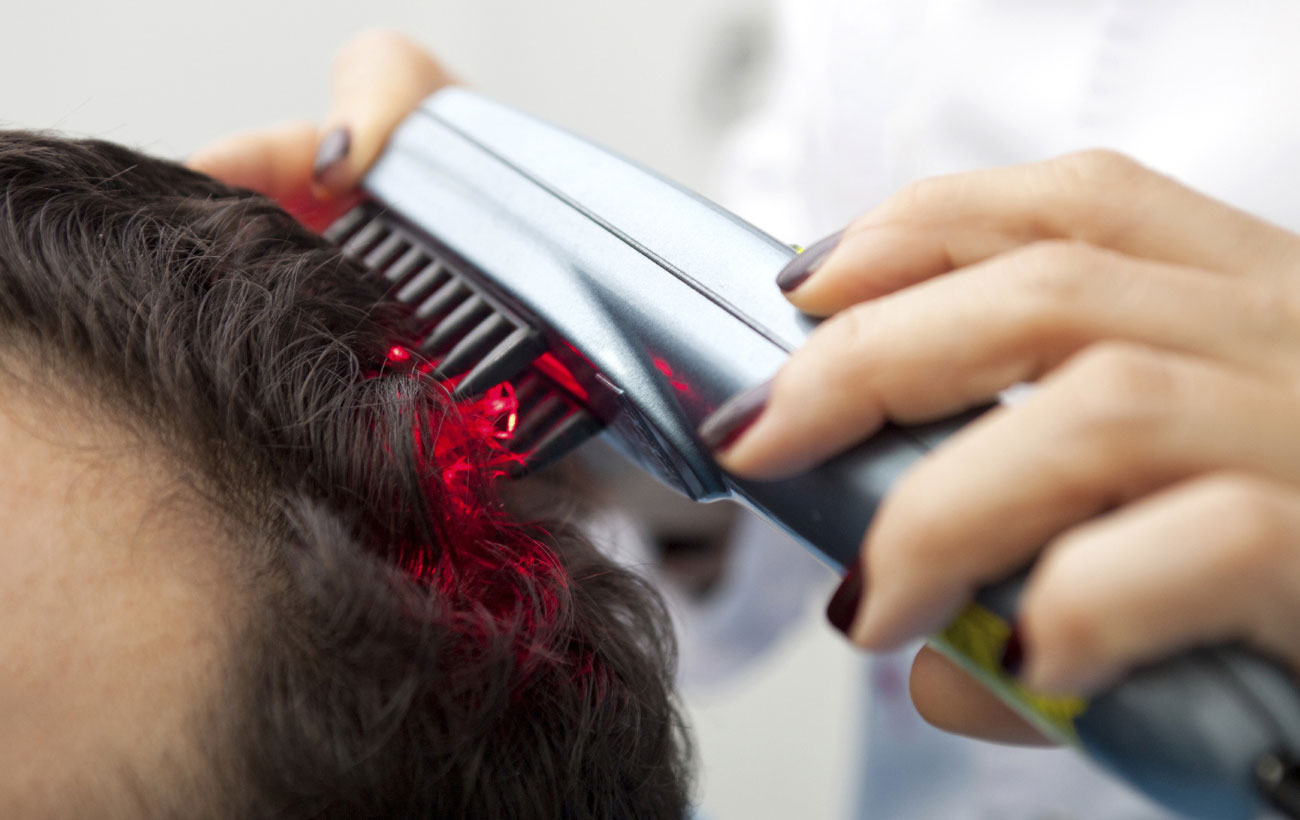
Surgical treatment includes (i) hair transplantation, a procedure where hair follicles are taken from the…
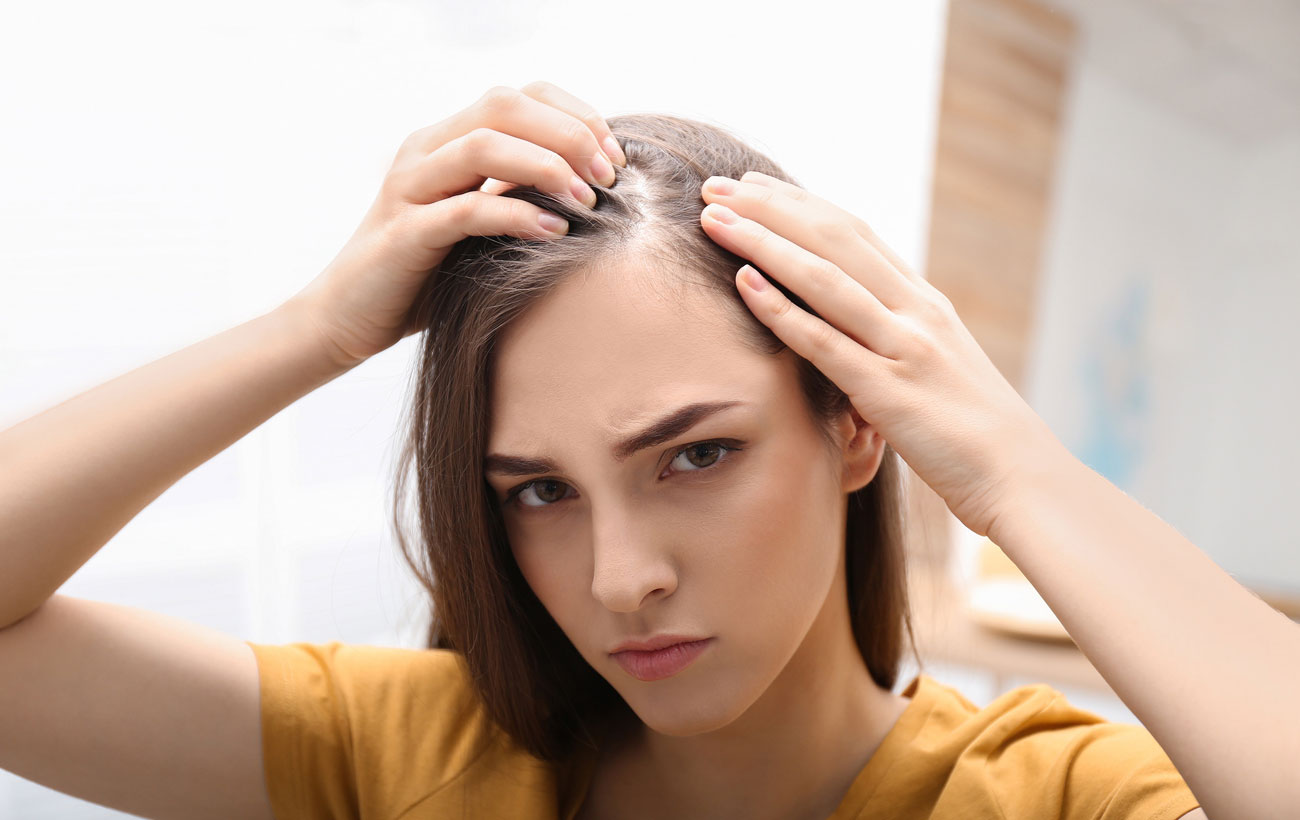

Female pattern hair loss (FPHL) has also been called androgenetic alopecia. It is the most common type of alopecia (hair loss) in women and the severity can vary.
Causes of female pattern hair loss
FPHL is caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors. The hairs produced by the affected follicles become progressively smaller in diameter, shorter in length and lighter in color until eventually the follicles shrink completely and stop producing hair. FPHL can be associated with conditions in which androgen (a group of hormones) levels are elevated such as polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). Acne, increased facial hair, irregular periods and infertility are all signs of PCOS.
Inheritance of female pattern hair loss
It is believed that it can be inherited from either or both parents.
Symptoms of female pattern hair loss
In women, the age of onset is later compared to male pattern hair loss, usually occurring in the 50s or 60s. Occasionally, FPHL in women may start earlier than this, in the 30s or 40s. FPHL is not usually associated with any scalp symptoms. Hair loss can, however, cause psychological consequences and have an impact on quality of life.
Diagnosis of female pattern hair loss
The diagnosis is usually based on the history of gradual thinning of hair or increased hair shedding on the top of the head, the pattern of hair loss and any family history of similar hair loss. The skin on the scalp looks normal on examination. Occasionally blood tests may be carried out.