innovative techniques Platelet-rich plasma therapy Times have changed since the days of bloodletting, when doctors…
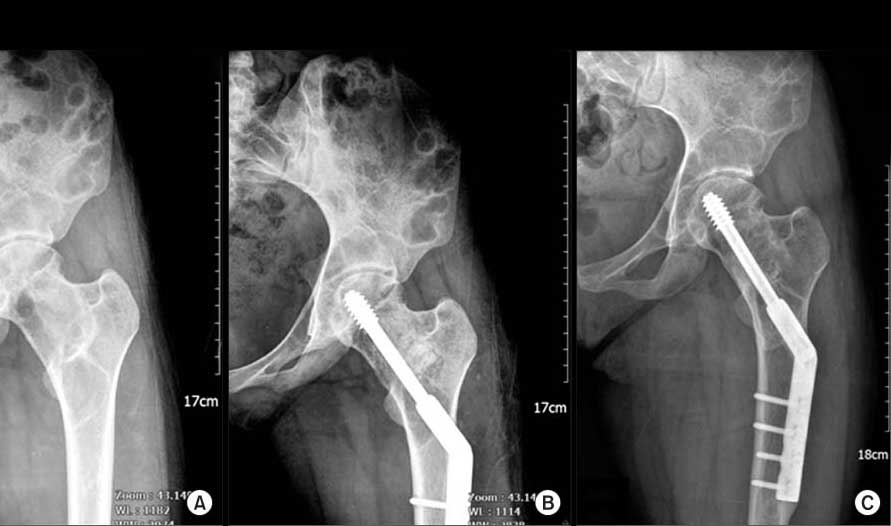
Fibrous Dysplasia
Fibrous dysplasia is a benign (non-cancer) chronic problem in which scar-like tissue grows in place of normal bone. It often results in 1 or more of these:
- Bone deformity
- Brittle bones
- Pain
- Uneven growth of bones
Any bone can be affected. More than 1 bone can be affected at any 1 time. When multiple bones are affected, often bones on 1 side of the body. However, fibrous dysplasia does not spread from one bone to another. The most commonly affected bones include:
- Facial bones
- Pelvis
- Ribs
- Shinbone (tibia)
- Skull
- Thighbone (femur)
- Upper arm bone (humerus)
- Vertebrae in the spine
Some people develop hormonal problems and a condition called McCune-Albright syndrome. McCune-Albright syndrome is another form of fibrous dysplasia. It causes different symptoms, such as early start of puberty and skin spots, called café-au-lait spots.
Fibrous dysplasia usually occurs in children ages 3 to 15. It is sometimes not diagnosed until adulthood. It is found equally in men and women and in all races.
Treatments
Treatment will depend on your symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is.
Treatment with surgery may include:
- Placement of a rod down the shaft of the bone
- Removal of affected bone, followed by bone grafting
- Removal of bone wedge
Other treatment may include:
- Medicines
- Pain management
- Physical therapy