Surgical treatment includes (i) hair transplantation, a procedure where hair follicles are taken from the…
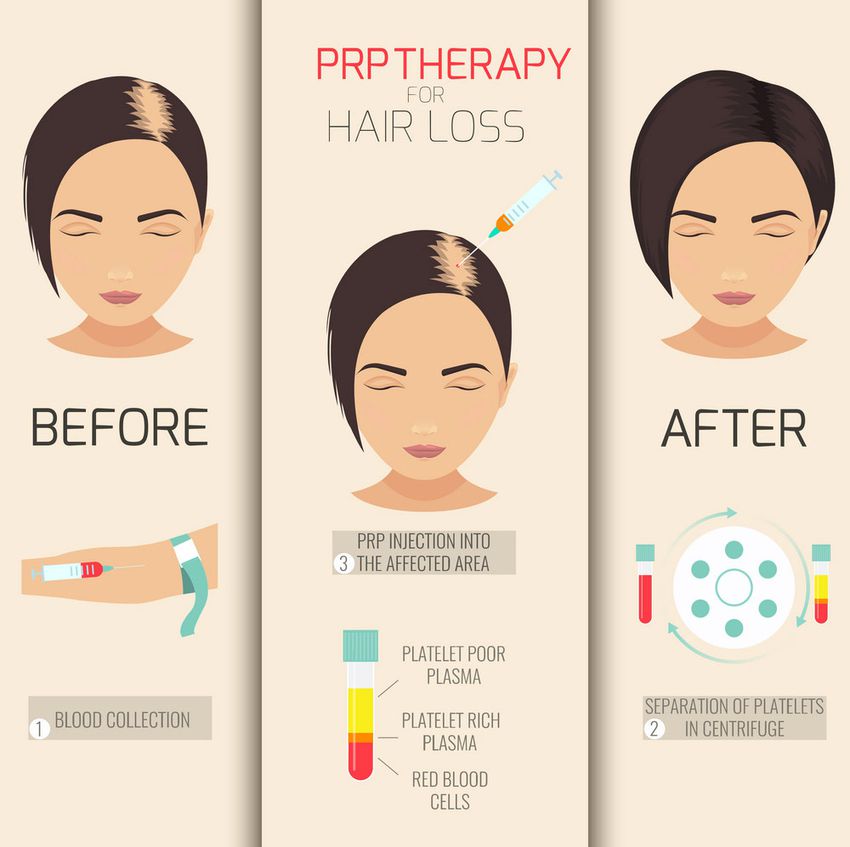
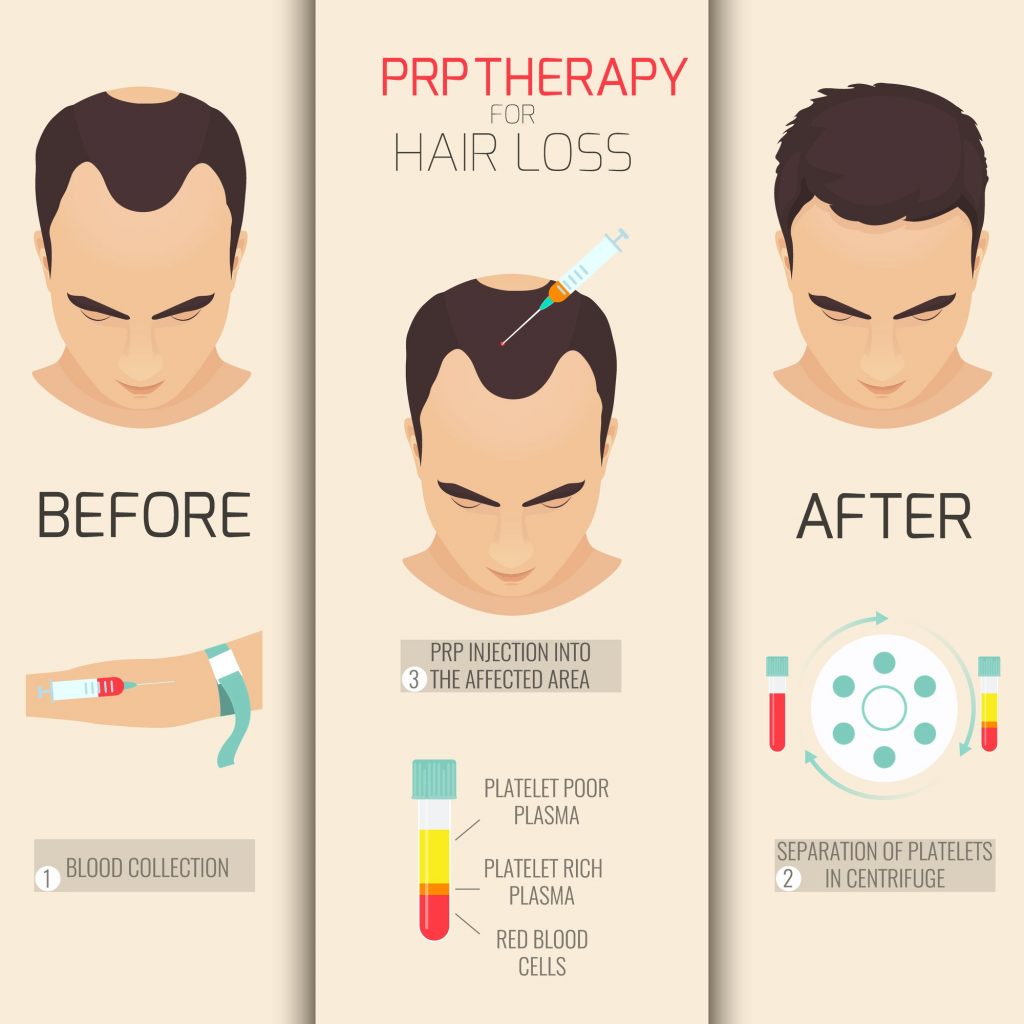
A Cell/Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP)
- Effectiveness of platelet rich plasma therapy
- Results of platelet rich plasma for hair loss
- Candidates for PRP
Platelet Rich Plasma, also known as PRP, and the addition of A-Cell™ is a non-surgical therapeutic hair restoration option. PRP has been in use in the medical field for two decades, and offers some promising potential for stimulating natural hair growth. However, no definitive studies yet exist that confirms its efficacy.
Effectiveness of platelet rich plasma therapy
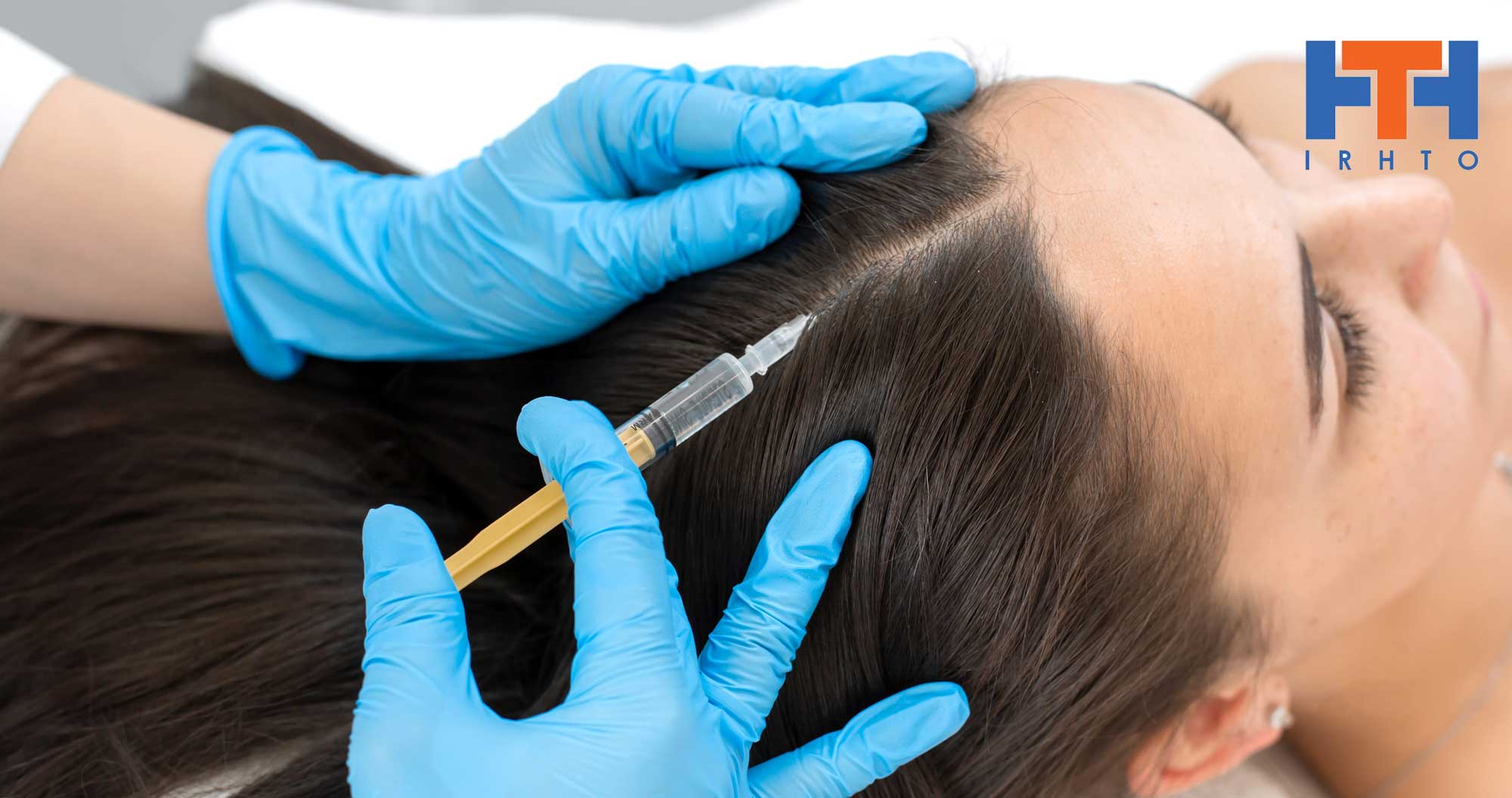
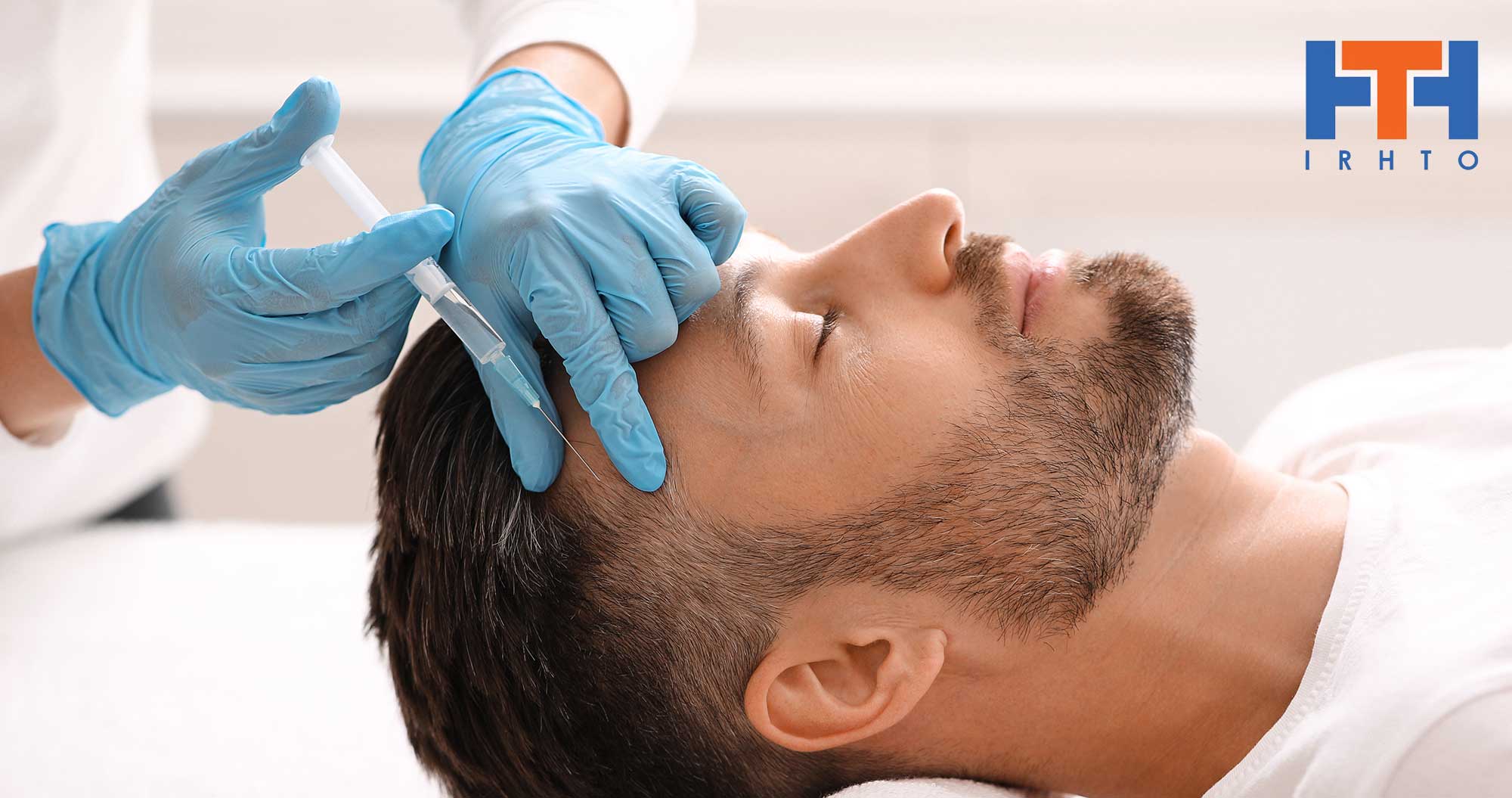
PRP works by stimulating newly implanted or inactive hair follicles into an active growth phase. Your blood contains small cells called platelets that help stop bleeding. Platelets also contain specific growth factors that when “activated” promote tissue regeneration and healing. These same growth factors may help hair grow or slow hair loss. Blood is drawn and then spun in a centrifuge, which has the effect of separating the platelet rich plasma from the rest of the blood. Local anesthesia is administered to the scalp so the patient feels no pain. The platelet rich plasma is then injected into the scalp. No sedation or medication is required. Early data suggests a regime of every nine to eighteen months is needed to achieve optimal stimulating results.
Results of platelet rich plasma for hair loss
Individual results vary. Extensive clinical studies are pending but the current medical literature contains numerous optimistic results. PRP should not be considered a “cure” for hair loss and no guarantee can be made about its individual effectiveness. PRP is not FDA-approved at this point in time.
Platelet rich plasma therapy for hair loss may be an option that is suggested by Dr. Vafaei during your personal consultation. In general, it is considered a complimentary procedure to other types of surgical or non-surgical hair restoration procedures.
You are not a candidate for PRP if you:
- Have medical conditions such as chronic liver disease, skin diseases or cancer, metabolic and systemic disorders
- Have undergone anti-coagulation therapy
- If you have any type of platelet dysfunction syndromes