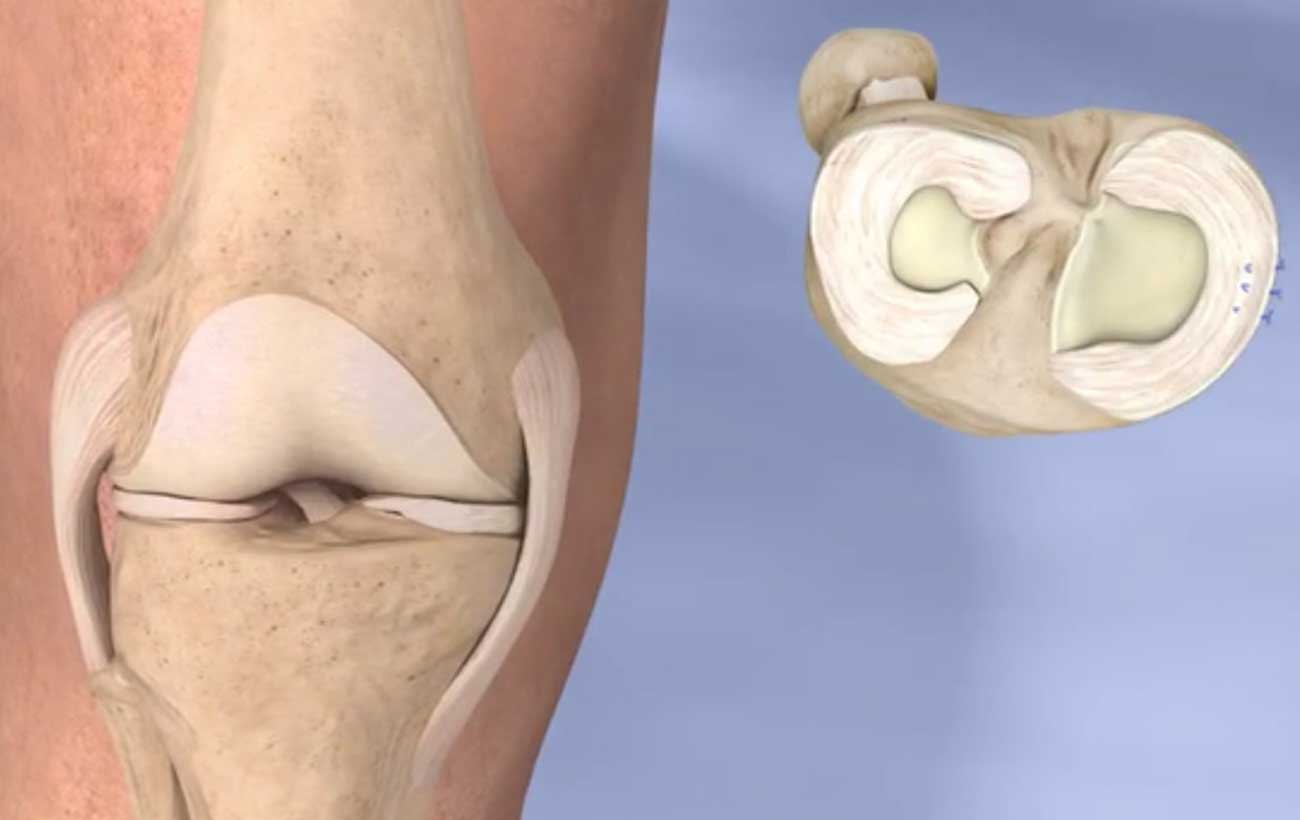
innovative techniques Platelet-rich plasma therapy Times have changed since the days of bloodletting, when doctors…
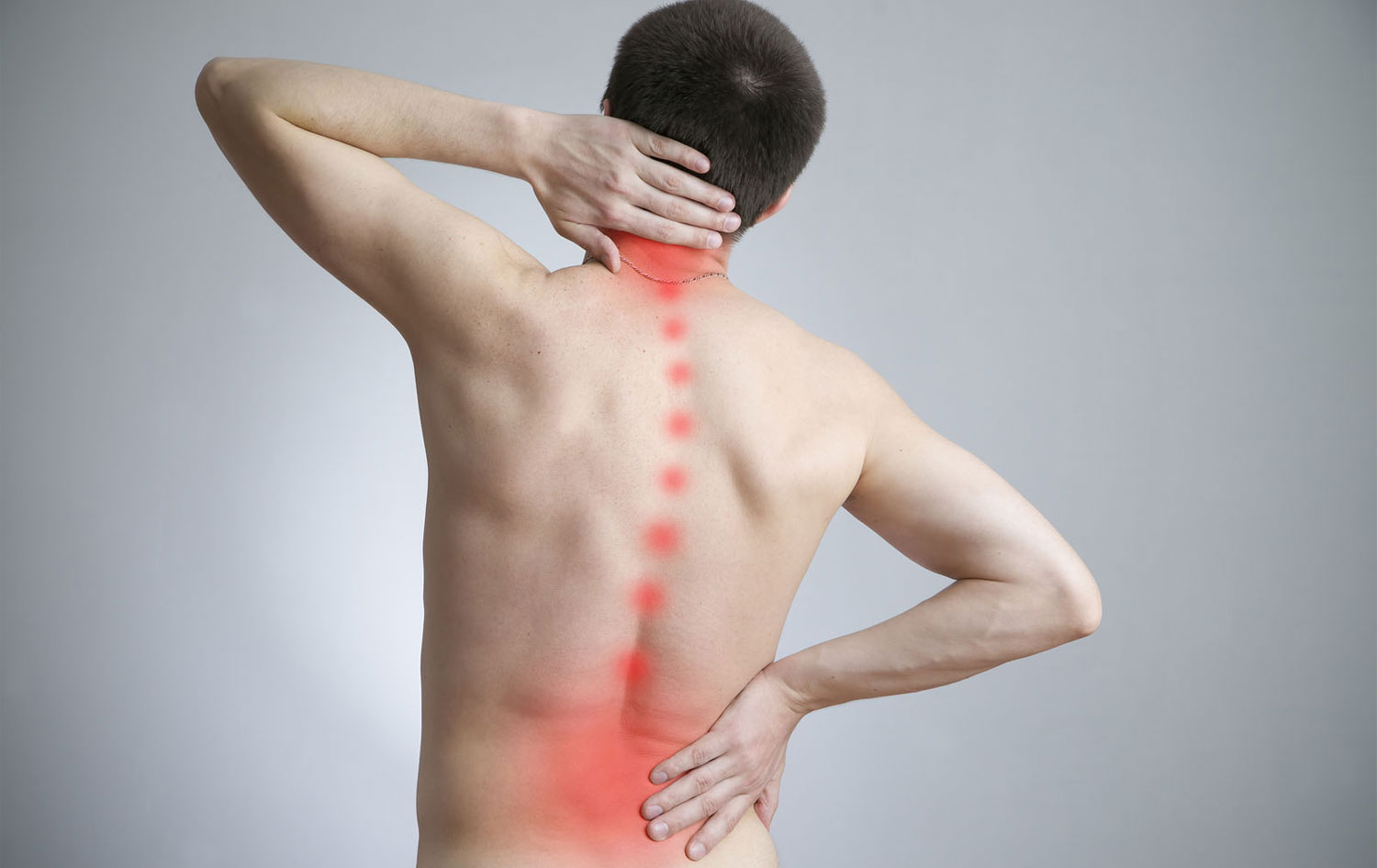
Back and Neck Pain
Back pain can range from a mild, dull, annoying ache, to persistent, severe, disabling pain. Pain in your back can limit your ability to move. It can interfere with normal functioning and quality of life. Always talk with your healthcare provider if you have persistent pain.
Neck pain occurs in the area of the cervical vertebrae in your neck. Because of its location and range of motion, your neck is often left unprotected and at risk for injury.
Pain in your back or neck area can come on suddenly and intensely. Chronic pain lasts for weeks, months, or even years. The pain can be constant or come and go.
Risk Factors
- Overuse, strenuous activity, or improper use, such as repetitive or heavy lifting
- Trauma, injury, or fractures
- Breakdown of vertebrae, often caused by stresses on the muscles and ligaments that support your spine, or the effects of aging
- Infection
- Abnormal growth, such as a tumor or bone spur
- Obesity. This put extra weight on your spine, and pressure on your disks.
- Poor muscle tone
- Muscle tension or spasm
- Sprain or strain
- Ligament or muscle tears
- Joint problems, such as arthritis
- Smoking
- Slipped disk (protruding or herniated disk) and pinched nerve
- Osteoporosis and compression fractures
- Problems of your vertebrae and bones that you were born with (congenital)
- Abdominal problems, such as an aortic aneurysm
Treatments
In many cases, acute back or neck pain may simply improve with some rest. Over-the-counter medicines such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen may also help with the discomfort. Try to move gently during this period, so that you won’t become stiff and lose mobility.
If you have chronic pain of your back and neck, try several remedies before considering surgery. These include:
- Hot or cold packs as advised by your healthcare provider
- Certain exercises to strengthen muscles and ease pain, such as stretching and flexing. Your healthcare provider can show you these exercises. Physical therapy can also help you find the correct exercises.
- Aerobic exercise may help with your overall fitness and strength
- Certain anti-inflammatory medicines or muscle relaxants may be used, as advised by your provider
- Braces or corsets for extra support
- Shots (injections) for pain relief in the area
- Nerve block. This eases pain signals from the affected nerve.
- Acupuncture
- Osteopathic manipulation
Prevention
The following may help to prevent back and neck pain:
- Practice correct lifting techniques. Don’t lift heavy items. When you do lift something, bend your legs, keep your back straight, and then slowly lift your body and the object.
- Wear a seat belt in motor vehicles in case of a collision.
- Use telephones, computers, and other equipment correctly.
- Maintain correct posture while sitting, standing, and sleeping.
- Exercise regularly. Learn back-strengthening exercises to keep your back muscles strong. Warm up with stretching exercises before doing back exercises.
- Do exercises that improve your balance.
- Don’t smoke.
- Stay at a healthy weight
- Reduce emotional stress that may cause muscle tension.
- Get enough vitamin D and calcium in your diet.