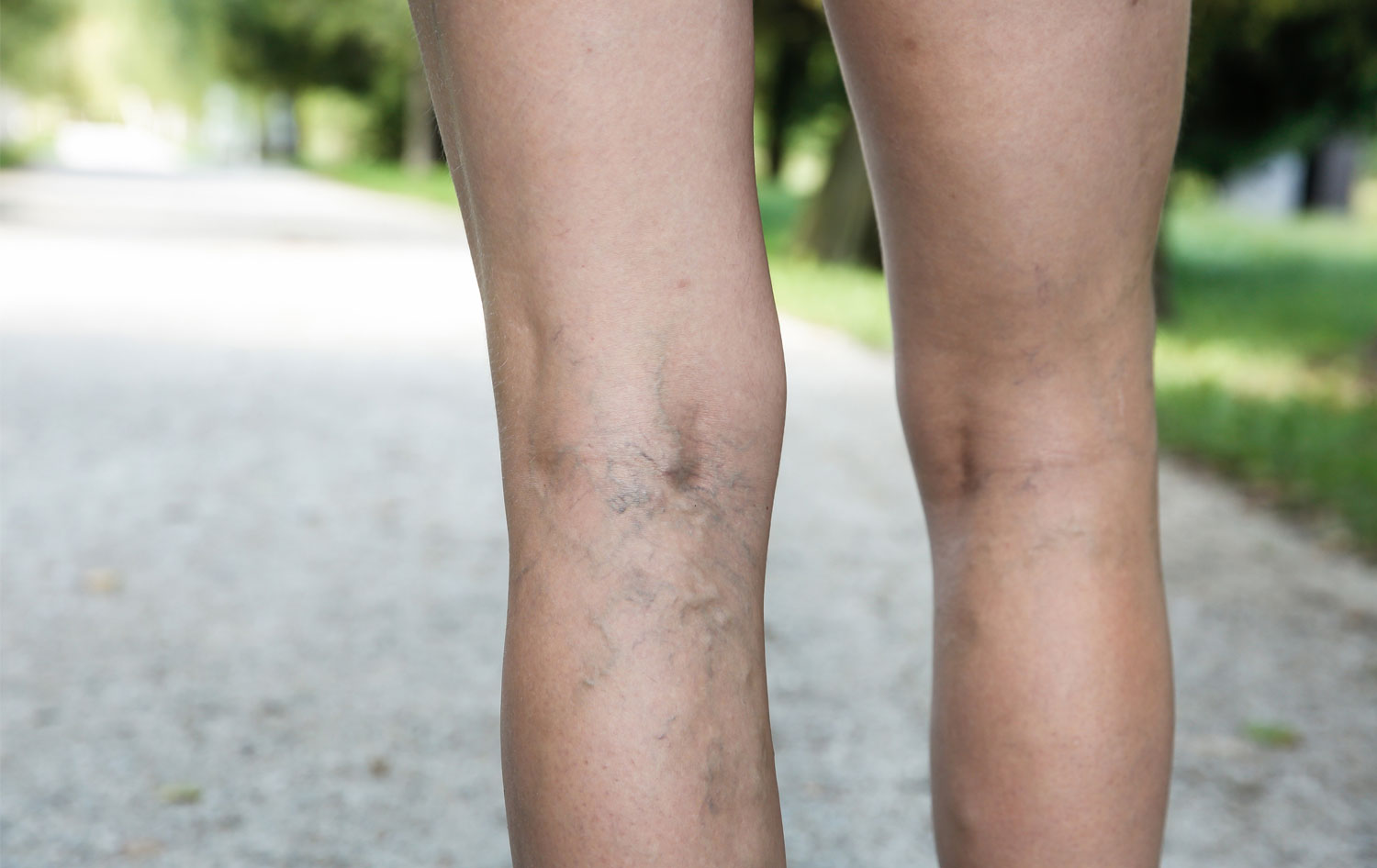
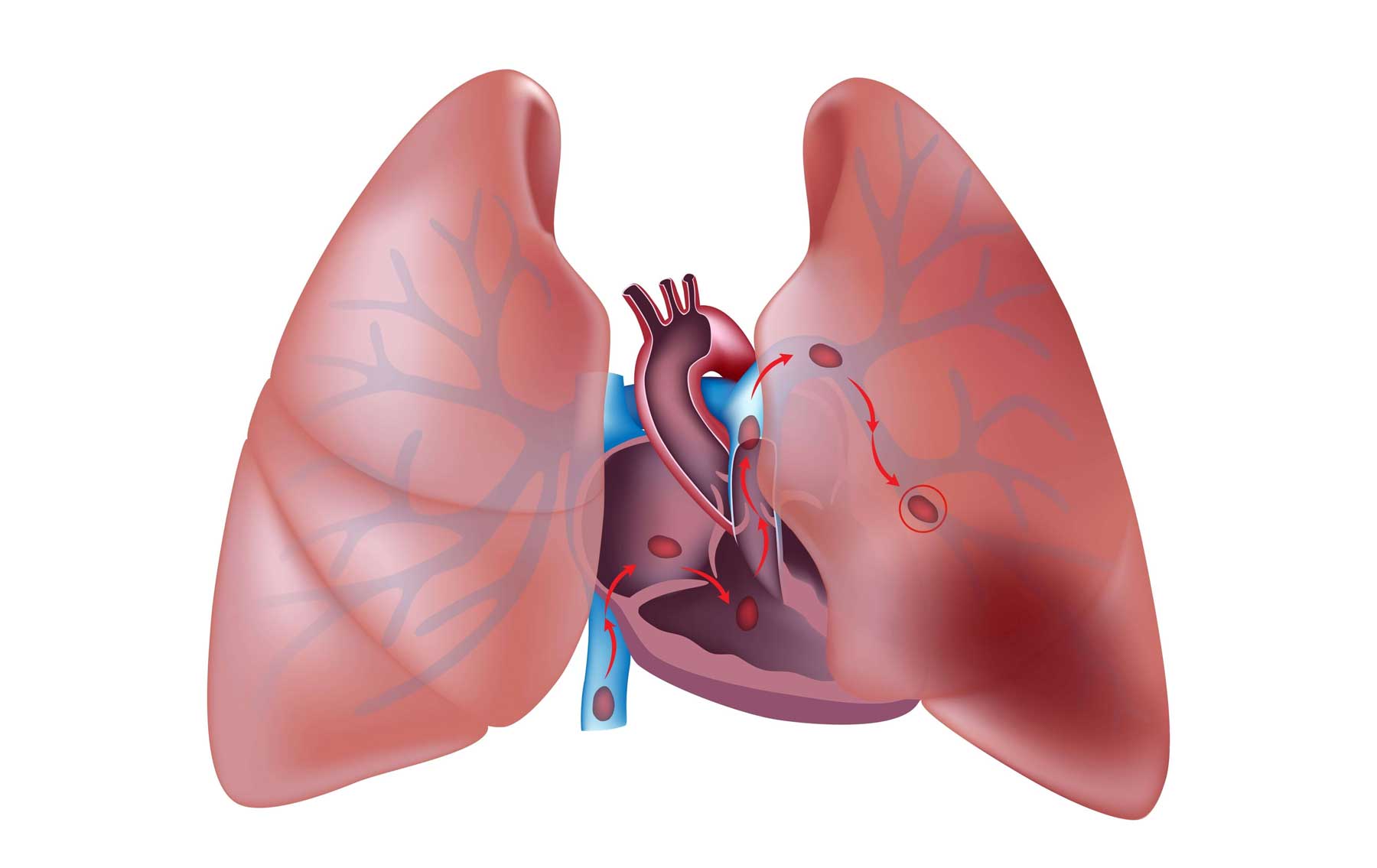
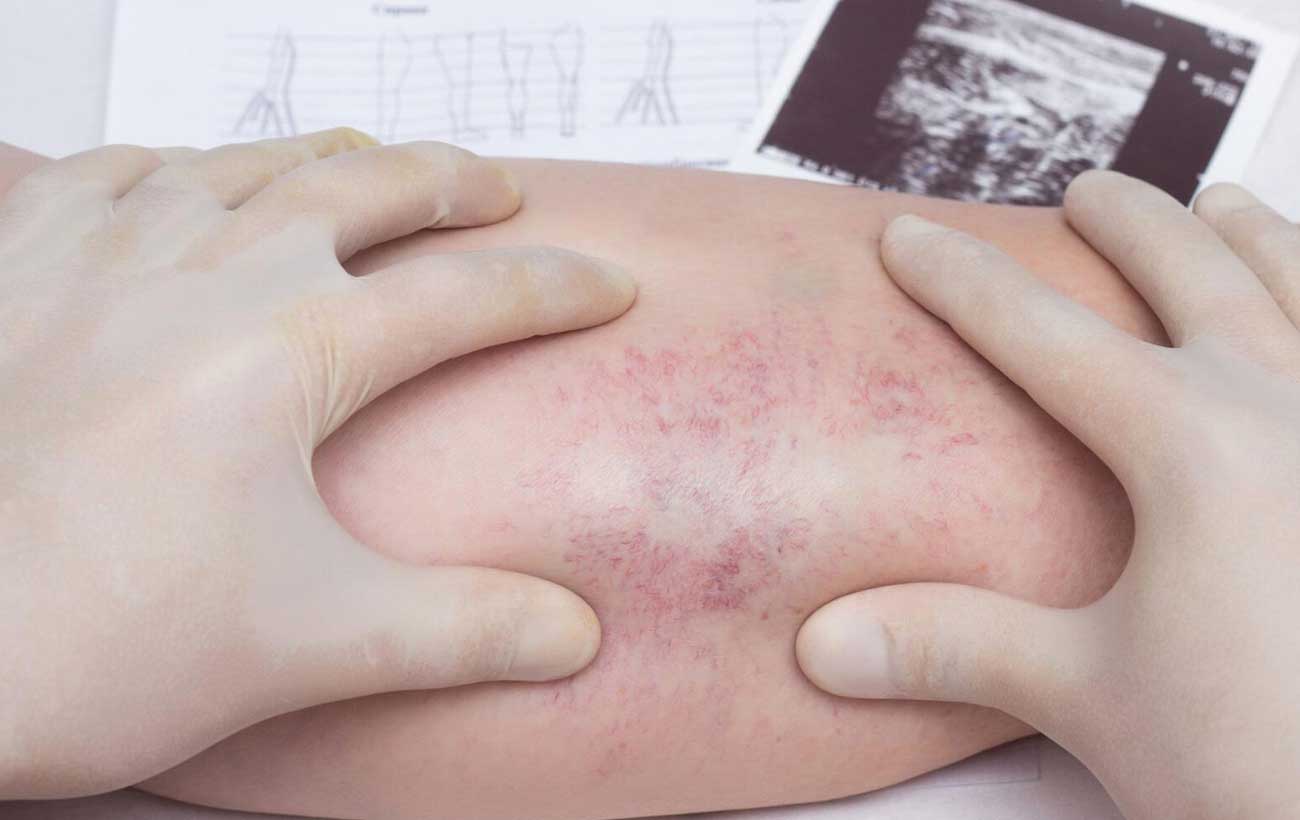
Deep Vein Thrombosis Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot (thrombus), which can partially…
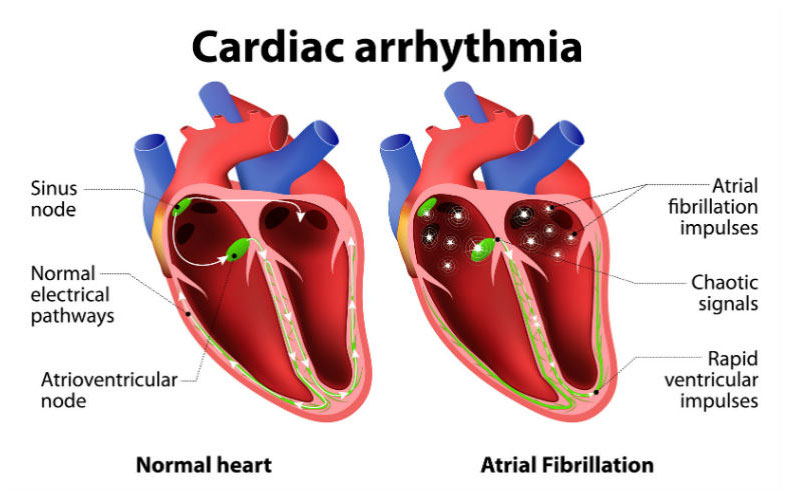
Arrhythmias
A normal heart rate for a person who is resting is between 60 and 100 beats per minute, with some minor variations. The two major types of arrhythmias are bradycardias, in which the resting heartbeat is slower than 60 beats per minute, and tachycardias, in which the resting heartbeat is faster than 100 beats per minute. An arrhythmia may be mild to severe and it may be continuous or alternate with periods in which the heart beats normally. A sudden, very rapid or very slow arrhythmia can reduce blood flow to the brain and may cause fainting or dizziness.
Risk Factors
In some cases, an arrhythmia may develop without an obvious underlying cause. Factors that increase the risk of arrhythmia include:
-
- Heart disease
- Congestive heart failure
- Heart valve disorders
- Overactive or underactive thyroid gland
- Chemical imbalances in the body
- Smoking
- Excessive intake of alcohol
- Excessive intake of caffeine
Symptoms
Arrhythmias, whether mild or severe, do not always cause symptoms. Because of this, even a life-threatening arrhythmia can go undetected. Possible symptoms of an arrhythmia include palpitations (heartbeats that you’re aware of), dizziness, fainting, shortness of breath, and angina (chest pain). An arrhythmia can sometimes be a symptom of a serious underlying disorder. If you have symptoms of an arrhythmia, see your doctor.
Treatments
Mild arrhythmias often do not require treatment. More severe arrhythmias and those that produce intolerable symptoms may be treated with beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, or medications that slow the heart’s electrical impulses. You may need to try several drugs before finding the medication that works best for you.
Some severe arrhythmias are treated surgically. Coronary artery bypass surgery and coronary angioplasty are sometimes used to treat arrhythmias that result from heart disease. A procedure called catheter ablation uses radiofrequency energy to destroy or remove a spot on the heart that is causing an arrhythmia. This procedure is similar to cardiac catheterization; a catheter is threaded into the heart, and the radiofrequency therapy is delivered through the catheter.
Many severe arrhythmias are treated by temporarily or permanently implanting an electronic pacemaker beneath the skin of the chest. A pacemaker is a battery-powered device that produces electrical impulses that regulate the heartbeat.