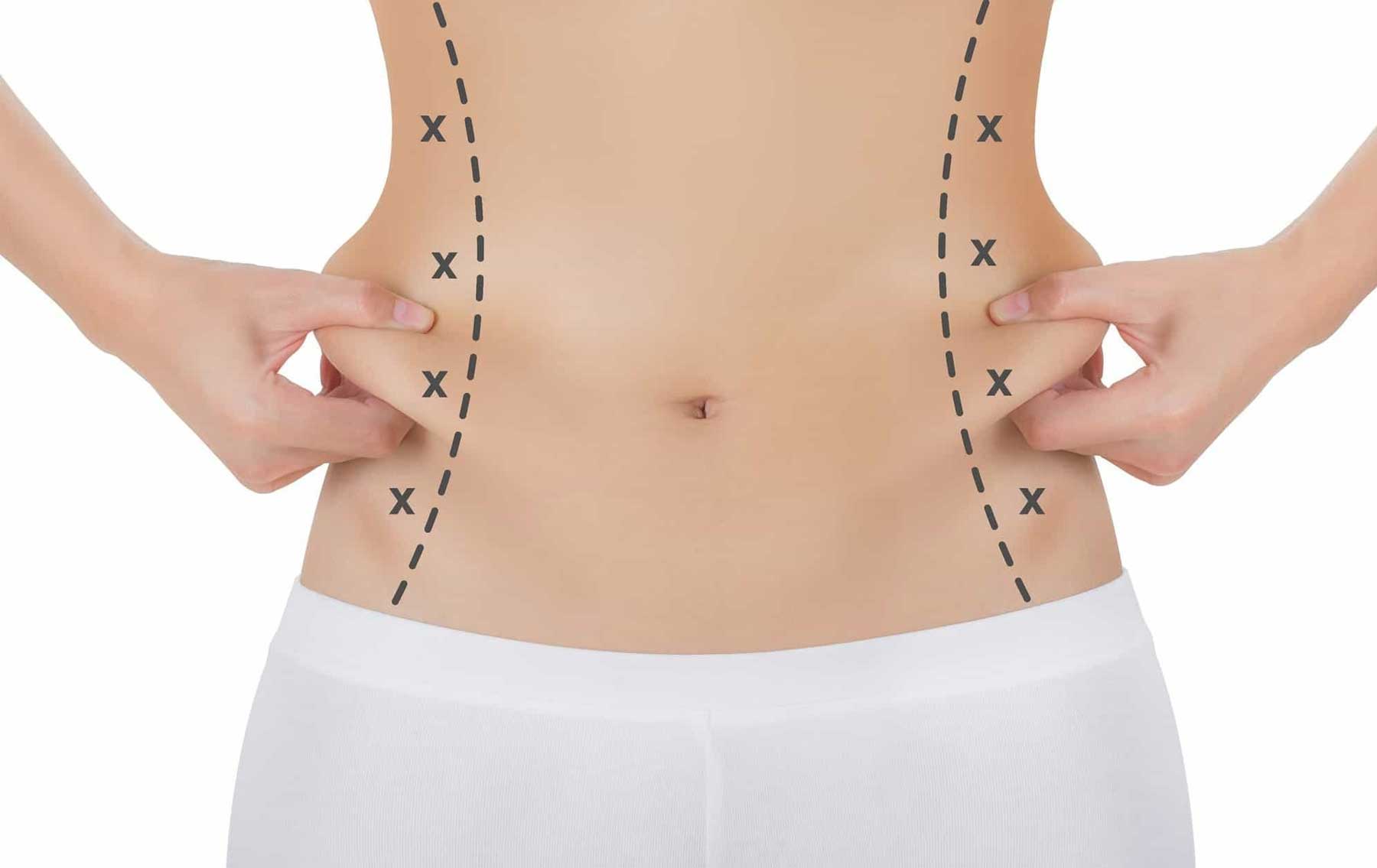
What is Liposuction
Liposuction, also called lipoplasty or suction lipectomy, reshapes the body by vacuuming out excess fat deposits. It is the most frequently performed cosmetic surgery procedure in the United States. Liposuction is not a substitute for weight loss but is designed to remove deposits of fat that persist despite diet and exercise. Using liposuction, a surgeon can remove unwanted fat from many parts of the body, including the abdomen, hips, buttocks, thighs, knees, calves, upper arms, chin, cheeks, and neck. The procedure works best on healthy people of normal weight who have firm, elastic skin.
Before surgery, your surgeon will evaluate your health, examine the fat deposits to be removed, and check the elasticity of your skin. Age is no barrier to liposuction, but older people tend to have looser skin and may not achieve the same effects as younger people. If liposuction is not appropriate for you, your surgeon may recommend an alternative method. For example, if you seek liposuction to reduce fat deposits in your abdomen, an abdominoplasty might be more effective.
Liposuction techniques are available that give surgeons more precise control and make recovery time faster. One such technique, called ultrasound-assisted lipoplasty, uses an instrument that produces ultrasonic (sound wave) energy. The sound waves explode the walls of fat cells and liquefy the fat so it can be removed more easily. This technique works best on the hips, abdomen, thighs, and neck.
In a procedure called fluid injection, the surgeon injects a solution containing medication and an anesthetic into the fat deposits to help ease their removal. Depending on the technique the surgeon uses, the amount of injected fluid may equal or be up to three times the amount of fat to be removed.
Liposuction Risks
The risks of liposuction increase with the size and number of areas to be treated. Although complications are rare, they can include infection or the formation of clots of fat or blood that can travel to the lungs and cause sudden death. Other risks include excessive fluid loss that can lead to shock, fluid accumulation in the lungs, burns or other damage to the skin or nerves, and injury to a vital organ. As with all cosmetic surgery, there may be imperfections in your final appearance, including baggy skin or an asymmetrical body contour. After the swelling goes down, you will begin to see the improvement in your body shape in 4 to 6 weeks.
The Procedure
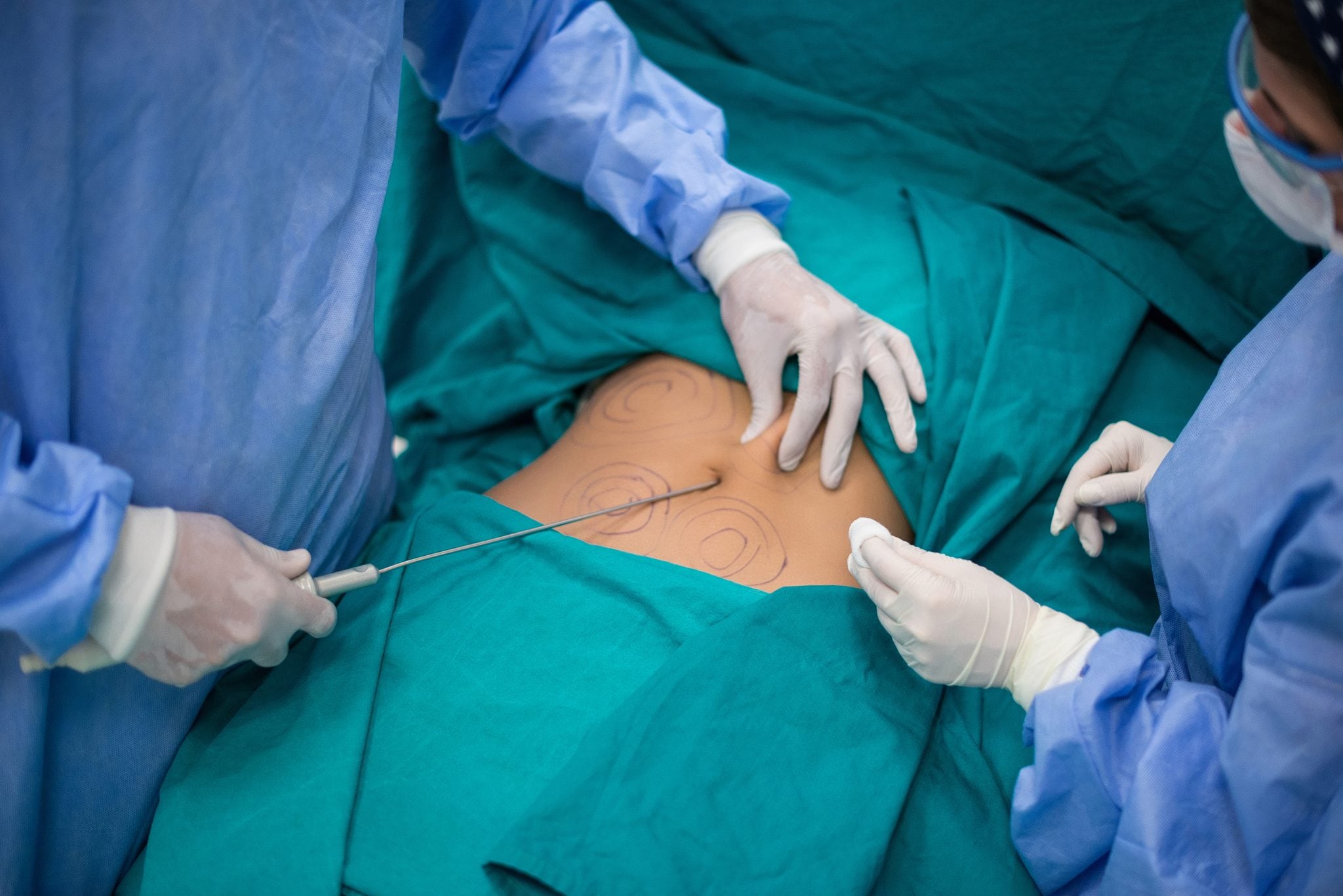
Liposuction is almost always performed as an outpatient procedure. Liposuction performed to remove small amounts of fat from only a few sites can be done using a local anesthetic, with or without light sedation. More extensive areas of the body are treated using regional anesthesia such as an epidural block, the same type of anesthesia used for pain management during delivery of a baby. Removal of a large amount of fat requires general anesthesia and intravenous fluids and, in some cases, a blood transfusion.
During a liposuction procedure, the surgeon makes a small incision in the skin over the area to be treated and inserts a narrow tube called a cannula under the skin. He or she pushes and pulls the tube through the underlying layer of fat and suctions the fat away with a vacuum pump or syringe. When one site is finished, the surgeon moves to the next area until all the designated areas are treated. The small incisions are closed with stitches. During and after surgery, you will be given intravenous fluids to replace the fluids that were suctioned out with the fat.
The amount of time needed to perform liposuction can vary substantially, depending on the volume of fat being removed, the number of body sites being treated, and the technique used. In general, liposuction takes from 1 to 4 hours.

After Liposuction Surgery
To prevent fluid buildup, the surgical team will probably insert small drainage tubes under your skin. You may have to wear a tight-fitting elastic garment over the treated area for a few weeks to help minimize swelling. Pain, burning, bleeding, bruising, and temporary numbness are common. Your doctor will probably prescribe medication to help relieve any discomfort, along with antibiotics to prevent infection. Most people who have liposuction can go back to work a few days after the procedure. The stitches are removed or will dissolve on their own in 7 to 10 days.

