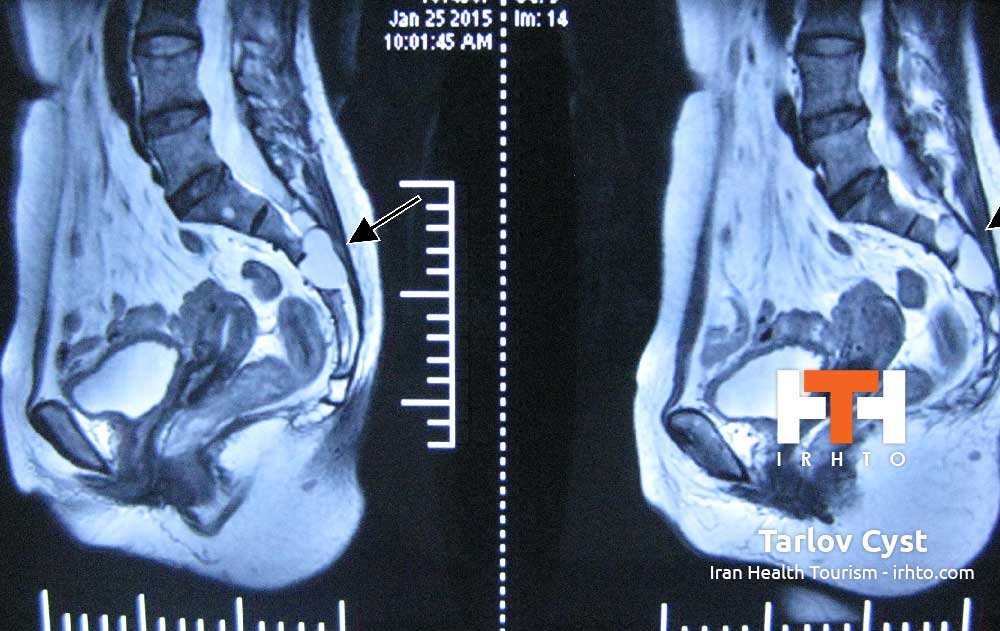
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is an abnormal lateral curvature of the spine. It is most often diagnosed in childhood or early adolescence. The spine’s normal curves occur at the cervical, thoracic and lumbar regions in the so-called “sagittal” plane. These natural curves position the head over the pelvis and work as shock absorbers to distribute mechanical stress during movement. Scoliosis is often defined as spinal curvature in the “coronal” (frontal) plane (The coronal plane is a vertical plane from head to foot and parallel to the shoulders, dividing the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) sections. The sagittal plane divides the body into right and left halves).
Causes
Scoliosis can be classified by etiology: idiopathic, congenital or neuromuscular. Idiopathic scoliosis is the diagnosis when all other causes are excluded and comprises about 80 percent of all cases. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis is the most common type of scoliosis and is usually diagnosed during puberty.
Congenital scoliosis results from embryological malformation of one or more vertebrae and may occur in any location of the spine. The vertebral abnormalities cause curvature and other deformities of the spine because one area of the spinal column lengthens at a slower rate than the rest. The geometry and location of the abnormalities determine the rate at which the scoliosis progresses in magnitude as the child grows. Because these abnormalities are present at birth, congenital scoliosis is usually detected at a younger age than idiopathic scoliosis.
Neuromuscular scoliosis encompasses scoliosis that is secondary to neurological or muscular diseases. This includes scoliosis associated with cerebral palsy, spinal cord trauma, muscular dystrophy, spinal muscular atrophy and spina bifida. This type of scoliosis generally progresses more rapidly than idiopathic scoliosis and often requires surgical treatment.
Treatments
Observation
In many children with scoliosis, the spinal curve is mild enough to not require treatment. However, if the doctor is worried that the curve may be increasing, he or she may wish to examine the child every four to six months throughout adolescence.
In adults with scoliosis, X-rays are usually recommended once every five years, unless symptoms are getting progressively worse.
Bracing
Braces are only effective in patients who have not reached skeletal maturity. If the child is still growing and his or her curve is between 25 degrees and 40 degrees, a brace may be recommended to prevent the curve from progressing. There have been improvements in brace design and the newer models fit under the arm, not around the neck. There are several different types of braces available. While there is some disagreement among experts as to which type of brace is most effective, large studies indicate that braces, when used with full compliance, successfully stop curve progression in about 80 percent of children with scoliosis. For optimal effectiveness, the brace should be checked regularly to assure a proper fit and may need to be worn 16 to 23 hours every day until growth stops.
Surgery
In children, the two primary goals of surgery are to stop the curve from progressing during adulthood and to diminish spinal deformity. Most experts would recommend surgery only when the spinal curve is greater than 40 degrees and there are signs of progression. This surgery can be done using an anterior approach (through the front) or a posterior approach (through the back) depending on the particular case.
Some adults who were treated as children may need revision surgery, in particular if they were treated 20 to 30 years ago, before major advances in spinal surgery procedures were implemented. Back then, it was common to fuse a long segment of the spine. When many vertebral segments of the spine are fused together, the remaining mobile segments assume much more of the load and the stress associated with movements. Adjacent segment disease is the process in which degenerative changes occur over time in the mobile segments above and below the spinal fusion. This can result in painful arthritis of the discs, facet joints and ligaments.
In general, surgery in adults may be recommended when the spinal curve is greater than 50 degrees and the patient has nerve damage to their legs and/or is experiencing bowel or bladder symptoms. Adults with degenerative scoliosis and spinal stenosis may require decompression surgery with spinal fusion and a surgical approach from both the front and back.