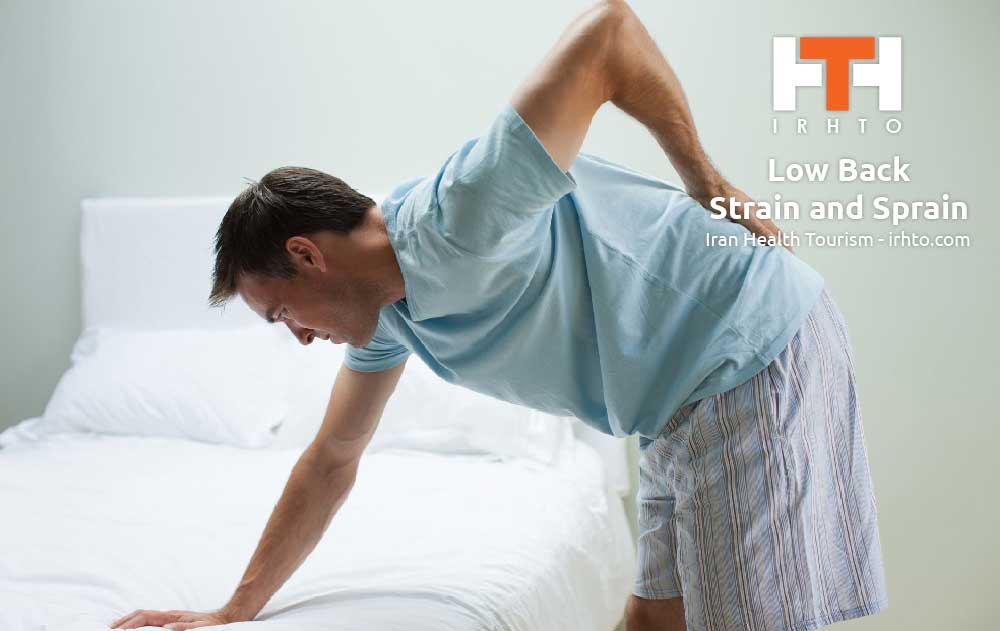
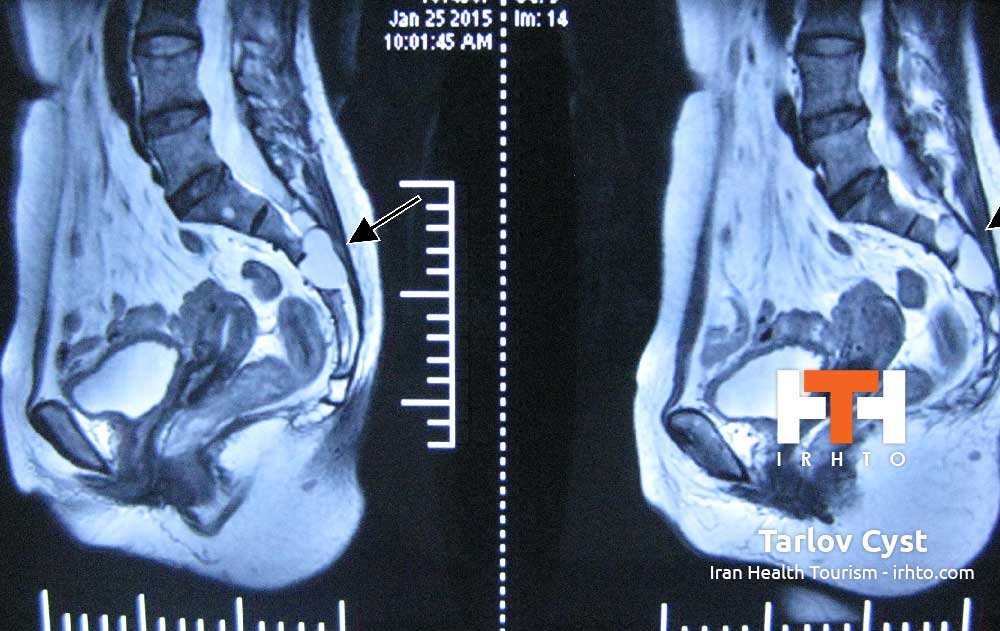
Low Back Strain and Sprain
Lumbar (lower back) muscle strains and sprains are the most common causes of low back pain. The back is prone to this strain because of its weight-bearing function and involvement in moving, twisting and bending. Lumbar muscle strain is caused when muscle fibers are abnormally stretched or torn. Lumbar sprain is caused when ligaments, the tough bands of tissue that hold bones together, are torn from their attachments. Both of these can result from a sudden injury or from gradual overuse.
When the lumbar spine is strained or sprained, the soft tissues become inflamed. This inflammation causes pain and may cause muscle spasms. Lumbar strain or sprain can be very debilitating.
Three types of muscles support the spine:
- Extensors (back muscles and gluteal muscles)
- Flexors (abdominal muscles and iliopsoas muscles)
- Obliques or rotators (side muscles)
Treatment [h4]
Bed rest is recommended for a short period of time, usually from one to three days. This should be as brief as possible, as prolonged bed rest can lead to a loss of muscle strength and may increase muscle stiffness, adding to pain and discomfort. Sprain and strain are commonly treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication if the pain is mild to moderate.
A doctor may recommend physical therapy. The therapist will perform an in-depth evaluation, which combined with the doctor’s diagnosis, will dictate a treatment specifically designed for patients with low back pain. Therapy may include pelvic traction, gentle massage, ice and heat therapy, ultrasound, electrical muscle stimulation and stretching exercises. Pain medication and muscle relaxants may also be beneficial in conjunction with the physical therapy.